Flood management measures
Adjustment of waterway
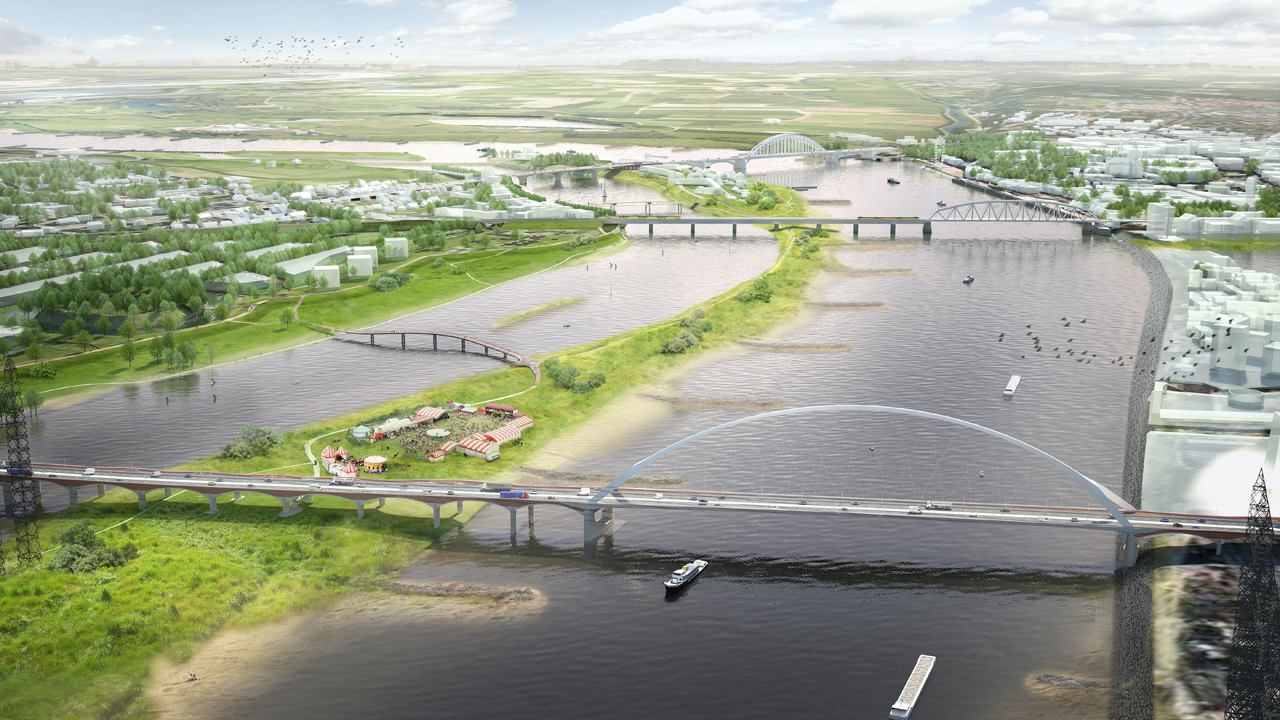

Adjustment of the waterway contains every constructional measure to a navigable channel, e.g. Broadening of curved waterways, deepening of the wat...
Afforestation

Land use conversion is a general term for large scale geographic change. Afforestation is one such land conversion in which trees are planted on pr...
Amphibious building
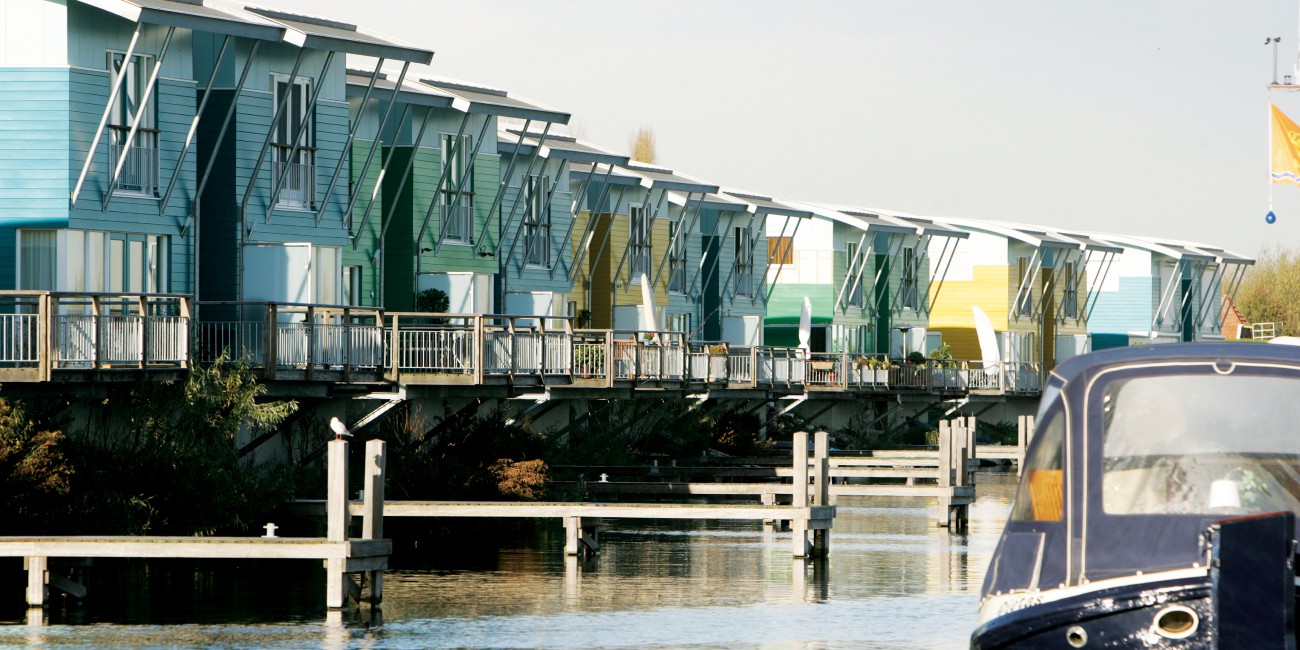

Amphibious buildings lie on the ground out of flood periods and are likely to float when the water level rises during flood. They do not therefore ...
Aquifer recharge
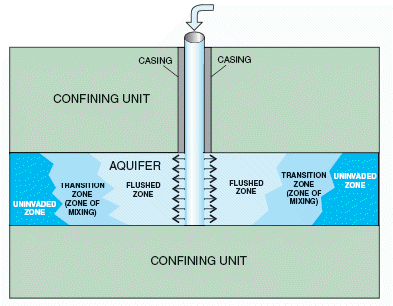
Aquifer recharge is achieved by adding surface water in basins, furrows, ditches, wells or other facilities where it infiltrates into the soil and ...
Artificial sand dunes and dune rehabilitation
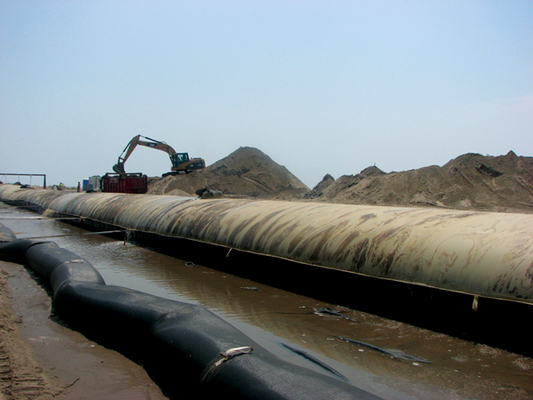

Naturally occurring sand dunes are wind-formed sand deposits representing a store of sediment in the zone just landward of normal high tides. Artif...
Beach nourishment

Beach nourishment is an adaptation technology primarily used in response to shoreline erosion, although flood reduction benefits may also occur. It...
Bioretention area
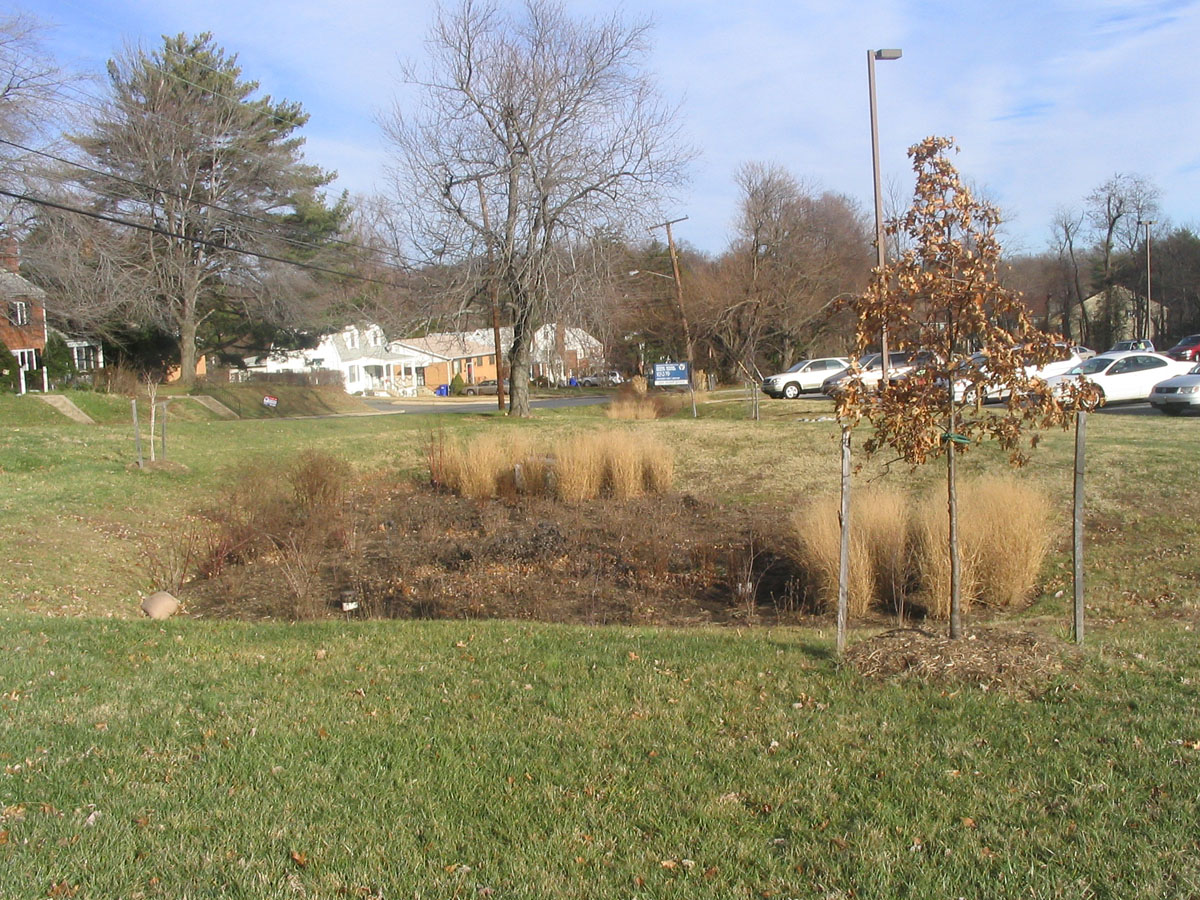

A bioretention area is a stormwater treatment system that is a depression integrated into the landscape. A bioretention area captures runoff from a...
Breakwater
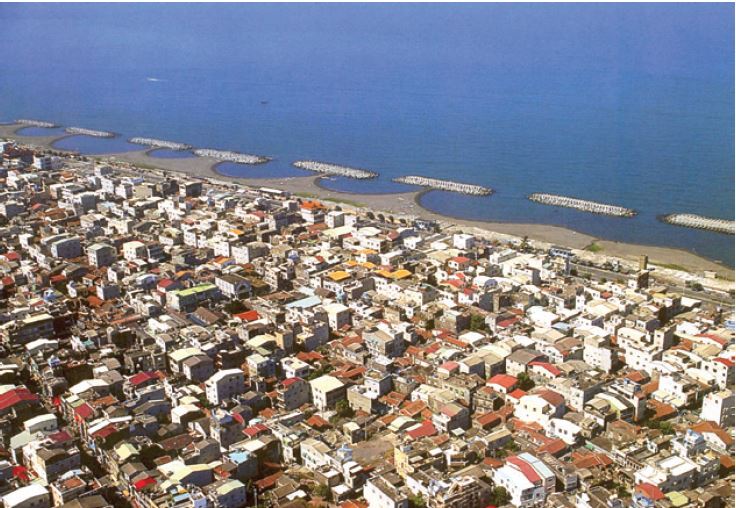

Breakwaters are structures constructed on coasts as part of coastal defense or to protect a port and port entrance from the effects of both heavy s...
Budget diversion
Governments of emerging-economy countries raise money for disaster response and rehabilitation by diverting funds from other budgeted items such as...
Building elevation
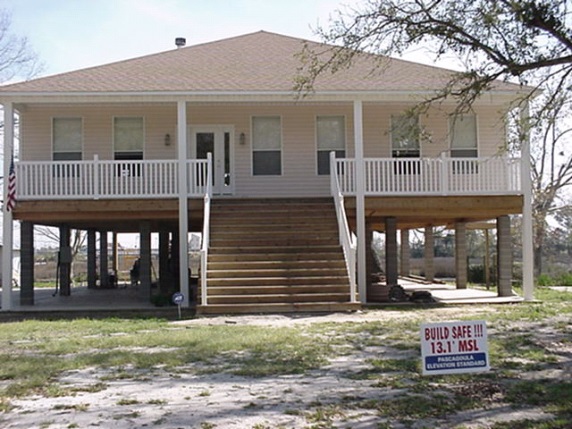

Building elevation is a measure mainly suitable for new constructions, but it can also be applied on existing buildings. The building is elevated t...
Building relocation

A building relocation is the process of moving a building from one location to another. There are two main methods for a building to be moved: disa...
Buildings as flood defence
New and existing buildings in flood risk areas can be used as flood defence. The buildings should be completely integrated in the flood defence to ...
Building without a crawlspace
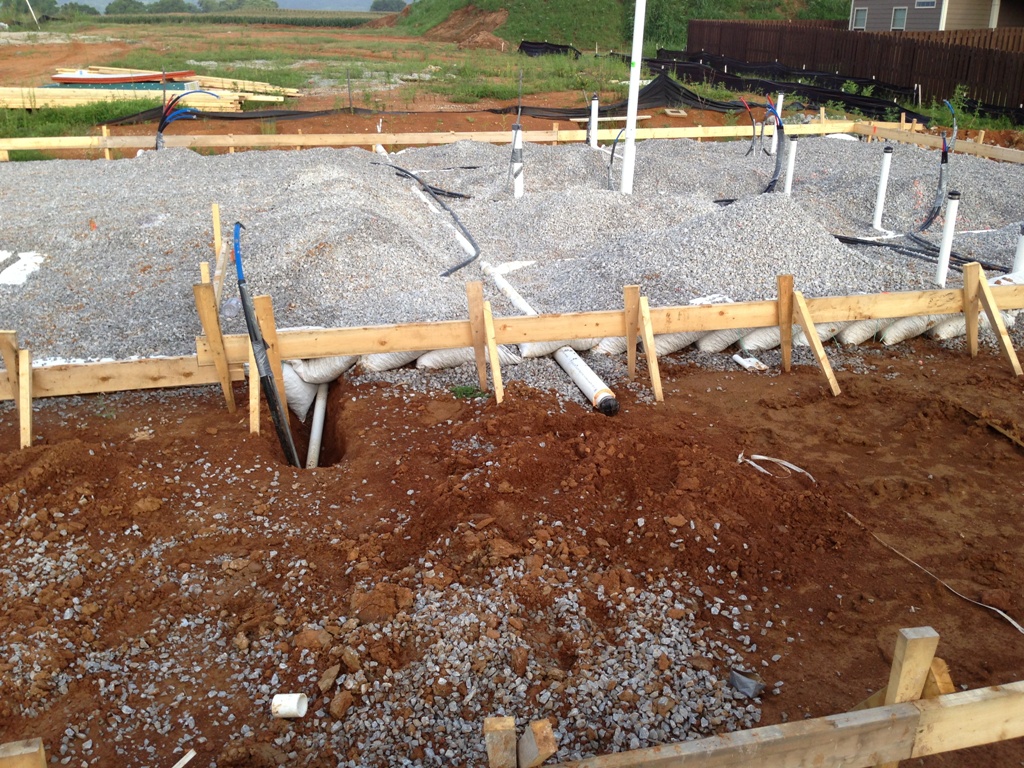

Crawlspaces vent the underside of a building and thereby prevent the moulding of dry wooden floors. However, with the introduction of concrete slab...
Bypass channel
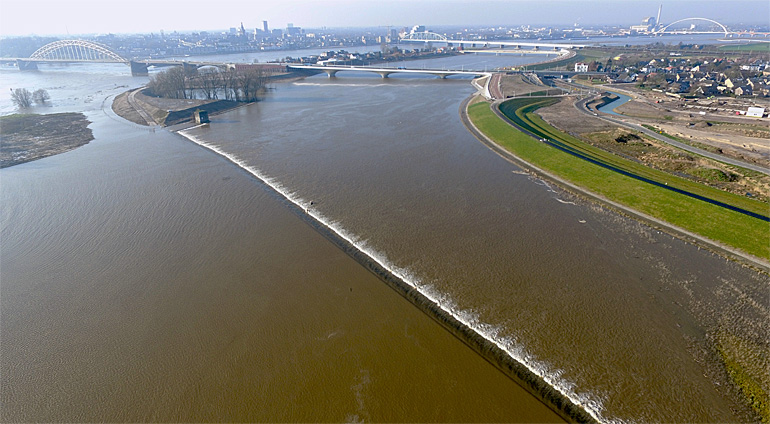

Bypass channel, also known as a flood-relief channel, is an artificially made waterway constructed in order to protect urban and rural agricultural...
Canal and rill

Canals and rills are open surface water channels with hard edges. They are simply channels that water flows along whereby they can have a variety o...
Cascading flood compartment system
The “system of cascading flood compartments” combines area prevention with constructional solutions. The idea is to (re)build a second dikeline of ...
Check valve

A check valve or non-return valve is installed in pipes which are vulnerable for backflow in flood conditions. Backflow is known to take place in t...
Coastal setback
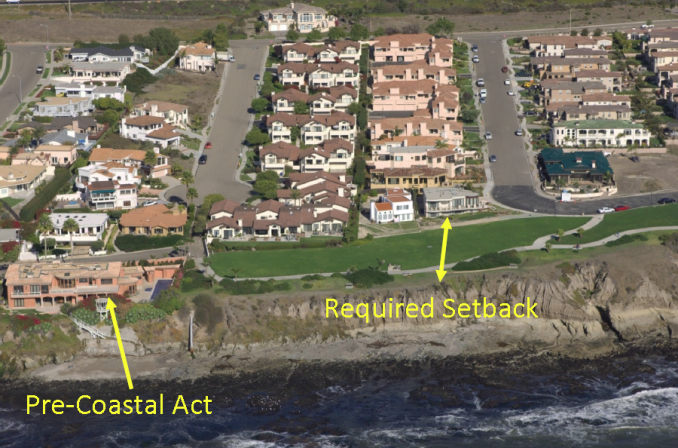

Coastal setbacks are a prescribed distance to a coastal feature such as the line of permanent vegetation, within which all or certain types of deve...
Community involvement
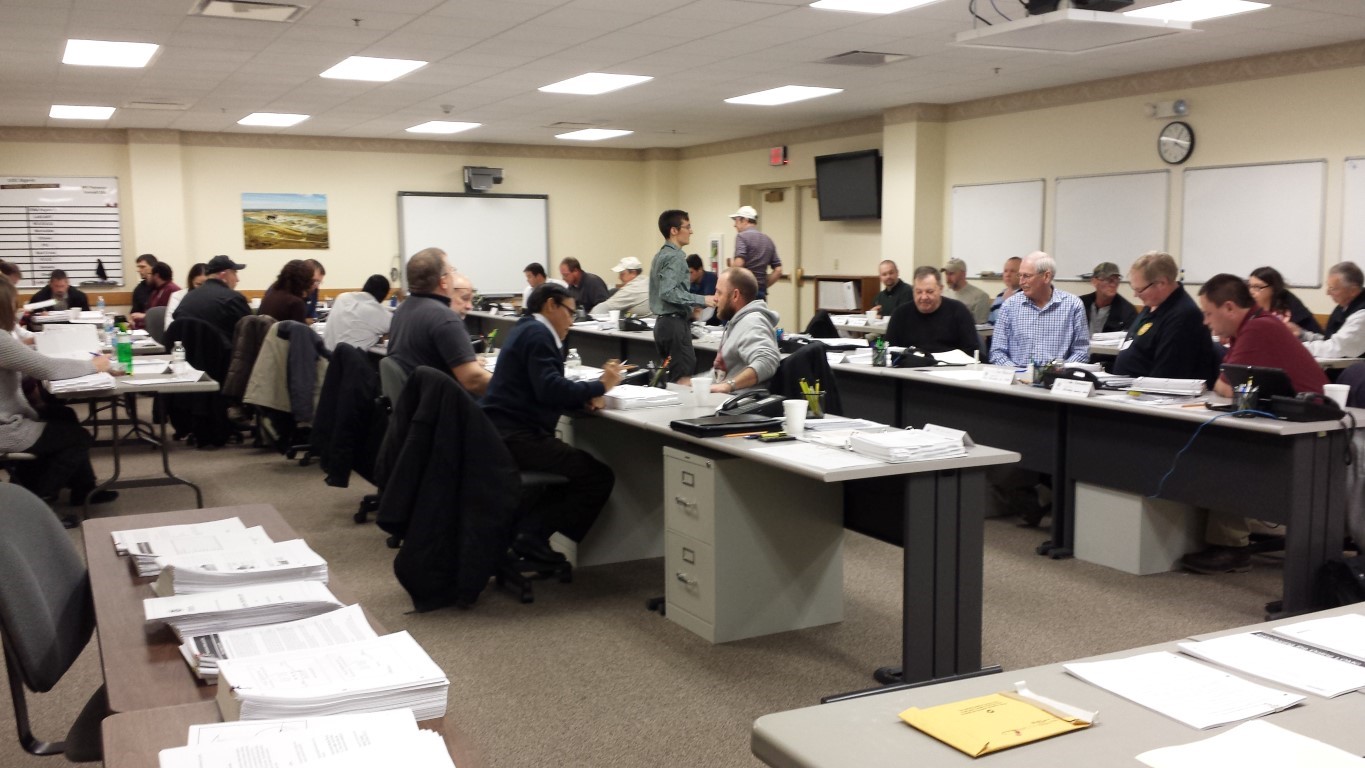

Community involvement is a bottom up approach which involves the community in decision-making process. For example, communities living in flood-pro...
Conventional urban drainage systems

The purpose of urban drainage systems (a.k.a. collection systems) is to enable safe and reliable disposal of stormwater runoff (i.e., they are at t...
Creation of a second dike line
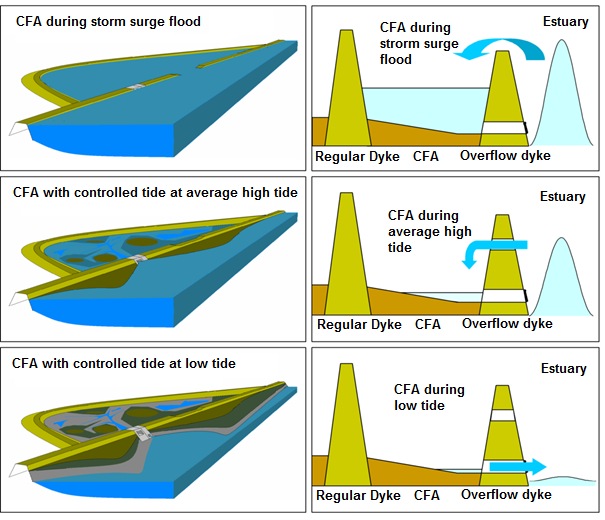
A second dike line is created by building other dikes, mostly bigger dikes, on the water side of existing dikes, which will not be removed. Buildin...
Data collection

Data collection is the process of gathering and measuring information on targeted variables in an established systematic fashion, which then enable...
Deculverting of watercourses
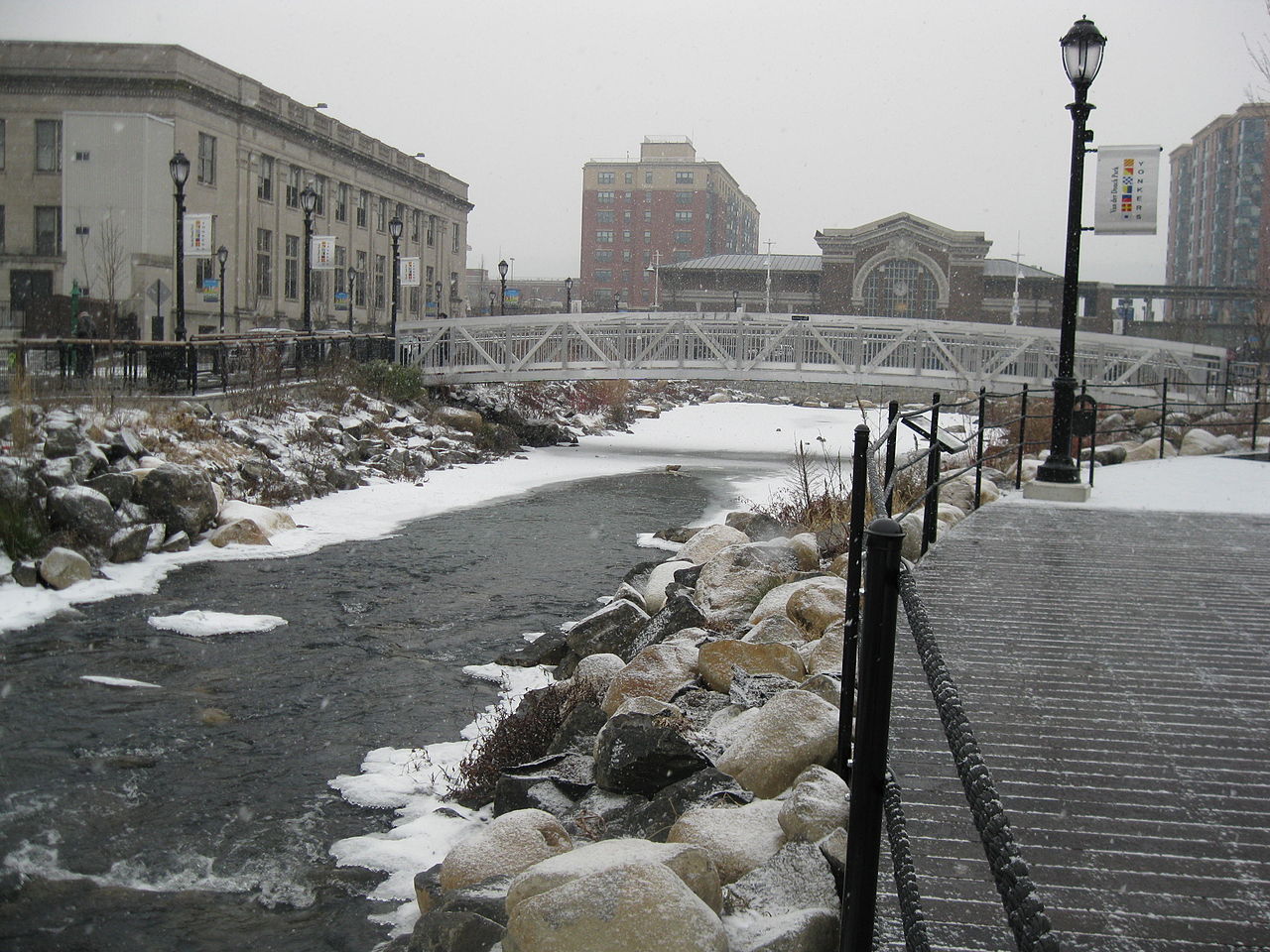

This activity involves techniques to resolve the issues created by culverted watercourses. This is predominantly through deculverting, or ‘daylight...
Demountable flood protection barrier
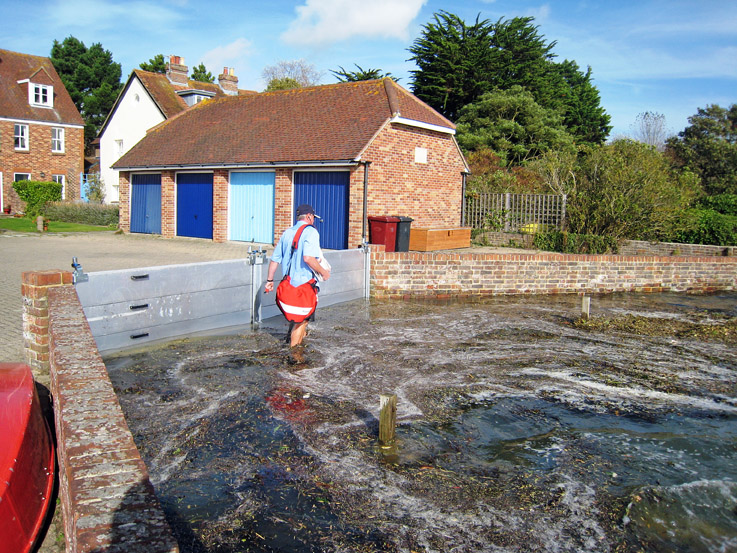

Demountable flood protection barriers consist of a combination of removable and pre-installed permanent components. The system is planned to be ere...
Dike

A dike or levee is an elongated artificially constructed embankment, which protects low-lying areas against higher water levels. It is usually made...
Dike inspection and/or recovery
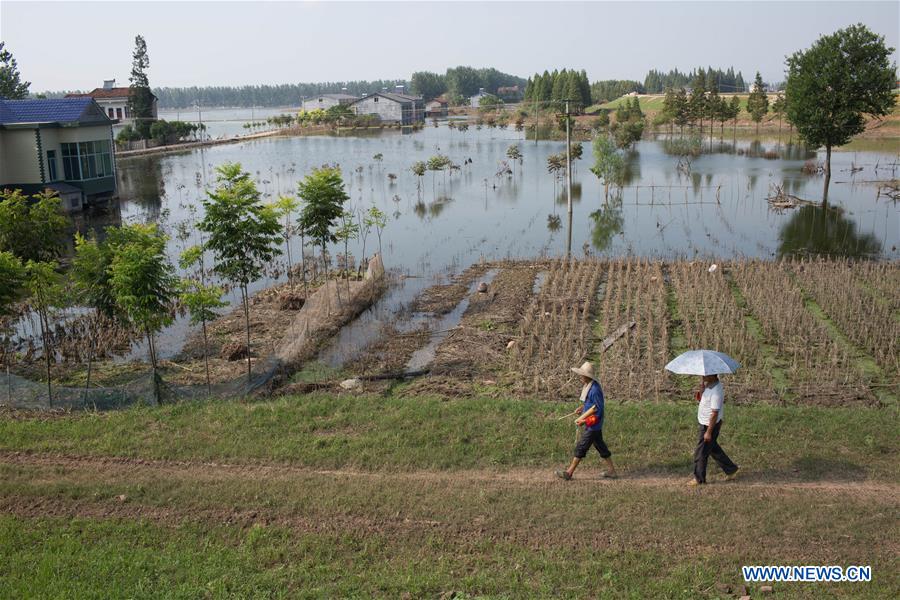

Inspection of the flood protection dikes takes place in order to observe and assess the state of the dike and especially after a storm surge events...
Dike reinforcement
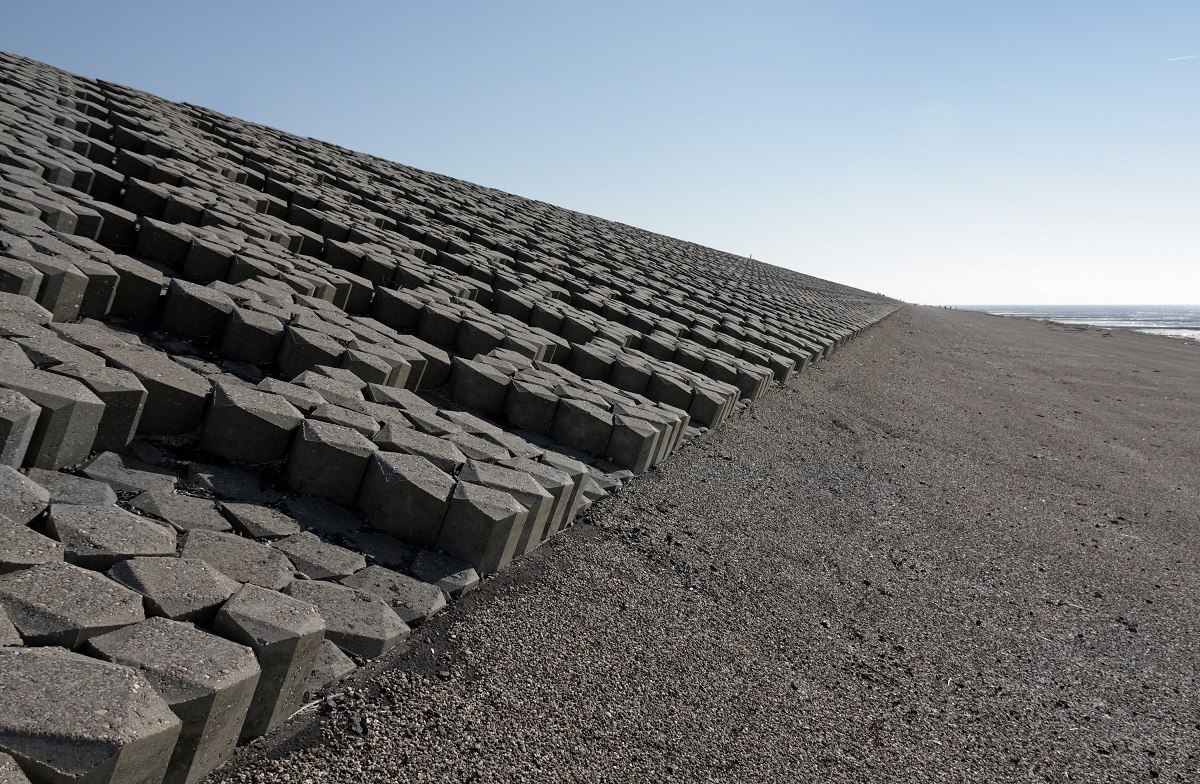

Dike reinforcement describes the process of strengthening the dike by e.g. raising the dike height, widening of the dike crest, broadening the who...
Dike relocation
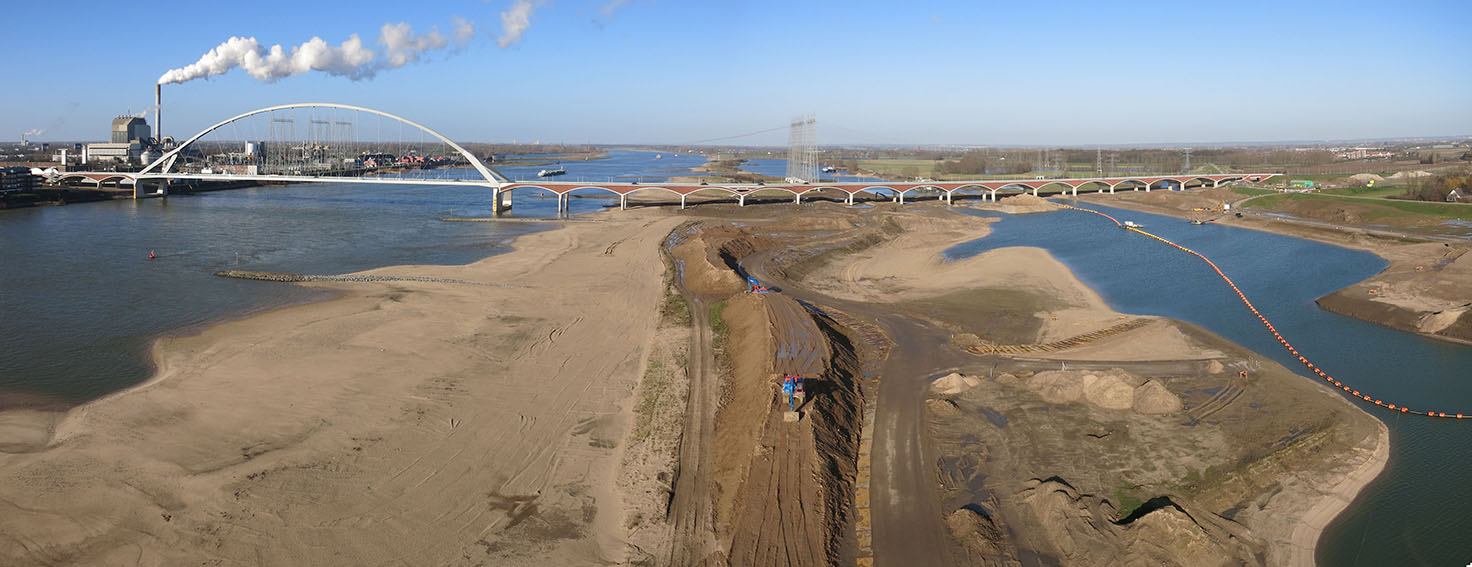

A new dike is built further away from the river or the coast after which the existing dike is removed. This leads to an increase of the flood plain...
Ditch
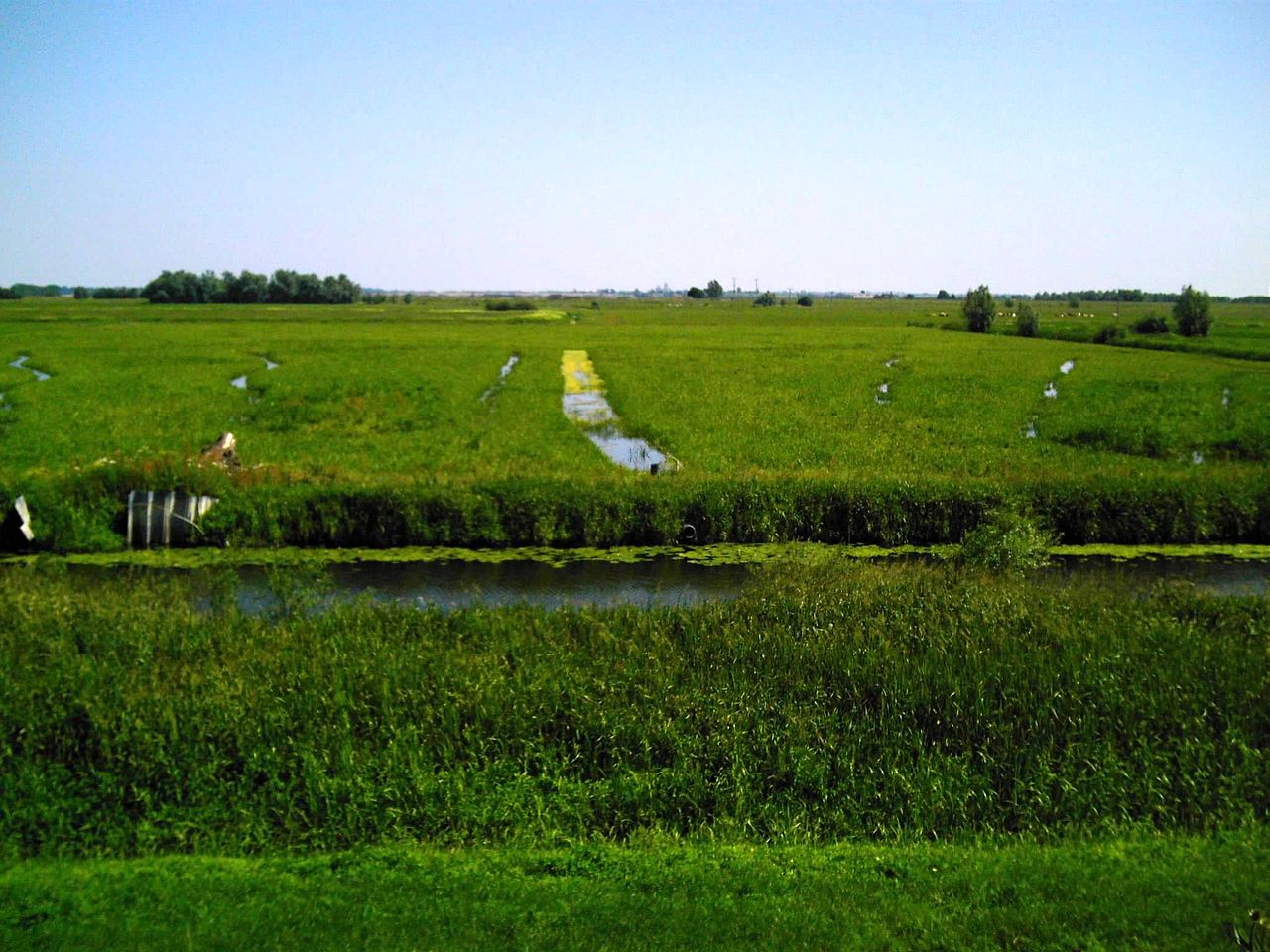

A ditch is usually defined as a small to moderate depression created to channel water. A ditch can be used for drainage, e.g. to drain water from l...
Dredging of watercourse
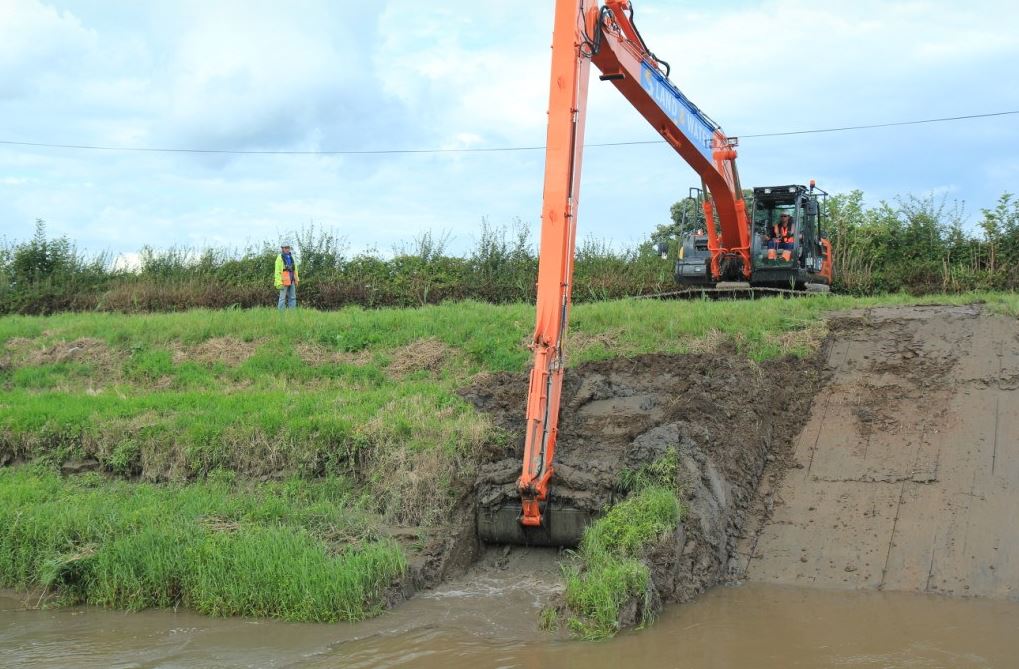

The term dredging is used to refer to the systematic removal of accumulated material from river or other watercourse channels. In its most extreme...
Dry-floodproofing technology
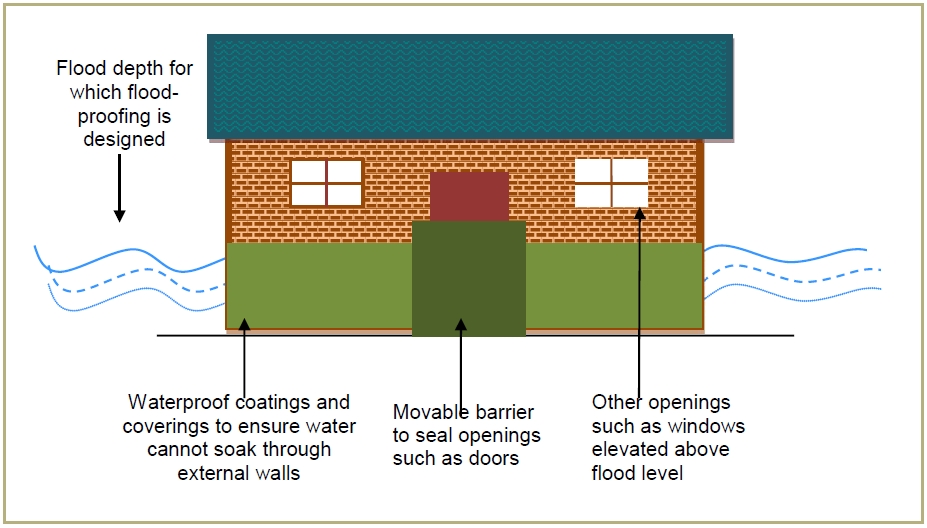
Dry floodproofing is a method of flood preparation that involves building designs and material choices that do not allow for the entry of floodwate...
Dwelling mound

A dwelling mound is an artificial hill made from earth, created to provide safe ground for humans and animals during storm surges. This concept ...
Elaboration of municipal archives on major hazards
Through municipal archives, citizens will be able to be kept informed about both the natural and technological risks to which the municipality has ...
Emergency exit of buildings above highest flood level

The main exit of a building is traditionally positioned at ground level. In case of a flood this only exit may be blocked by water and debris taken...
Emergency operation centre and personnel
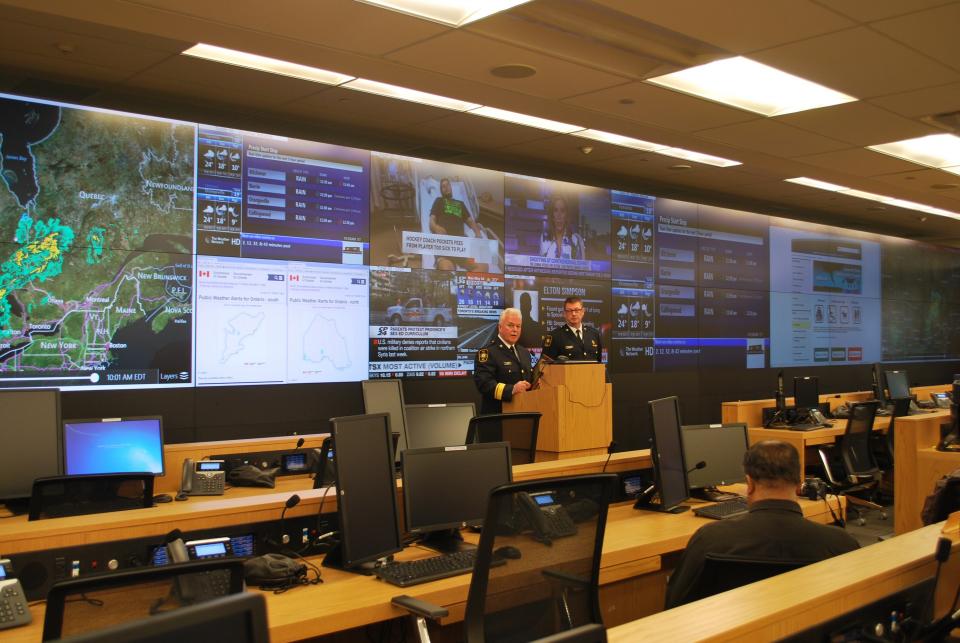

An Emergency Operation Centre (EOC) is a central location where response personnel can coordinate and make decisions in support of emergency respon...
Emergency supplies and utilities
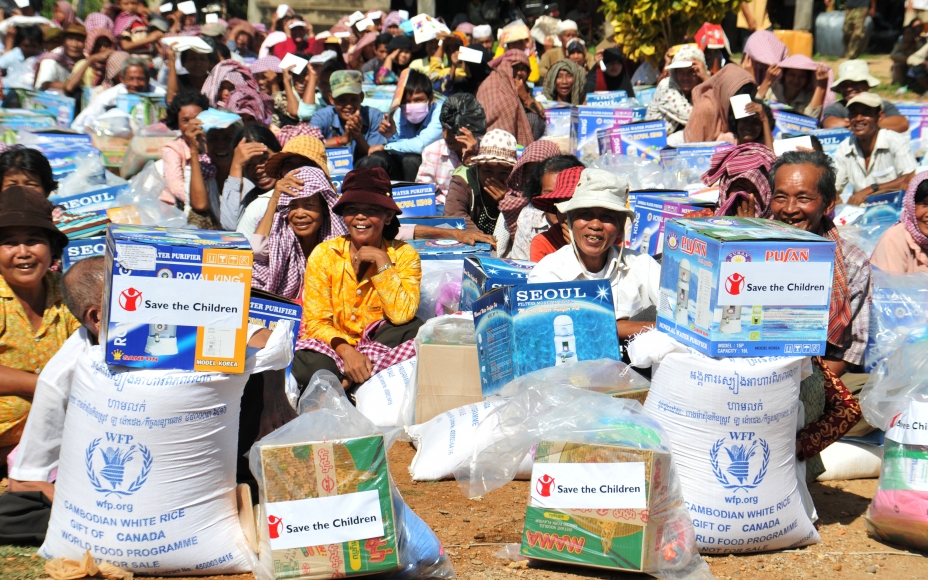

Emergency supplies and utilities are necessary in case of a flood emergency. It should consist of food and drinks, first aid kit and other provisio...
EU Flood Risk Management Directive

EU adopted the Flood Risk Management Directive. Directive 2007/60/EC on the assessment and management of flood risks entered into force on 26 Novem...
Evacuation plan
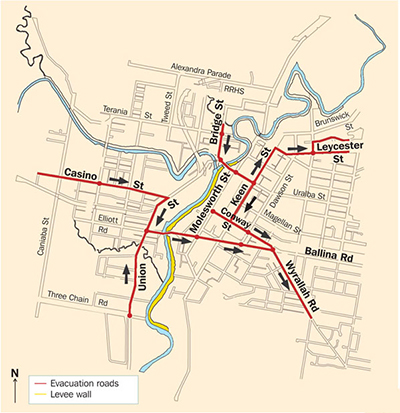
The purpose of evacuation is to relocate people temporarily from areas at risk of the consequences of flooding to places of safety. Emergency evacu...
Evacuation routes at elevated level
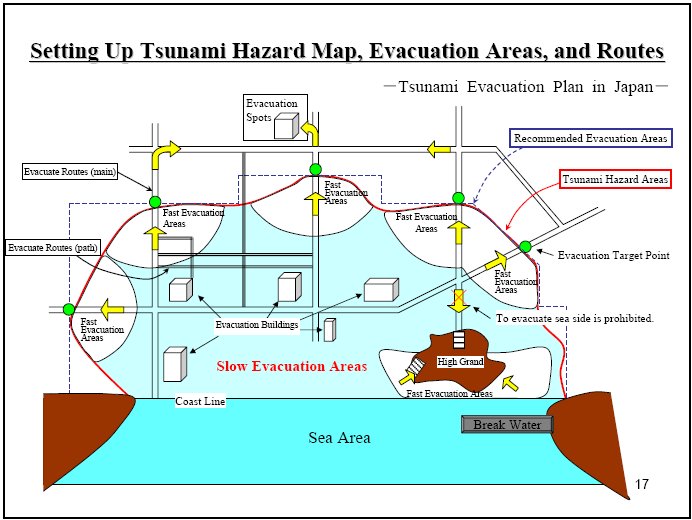
Evacuation routes at an elevated level are necessary as a route for safe evacuation in flood events. They should be constructed above the highest e...
Family emergency planning

Disasters and emergencies such as floods can affect people in any part of the world and at any time of the year, swiftly and without warning. Even...
Fascine
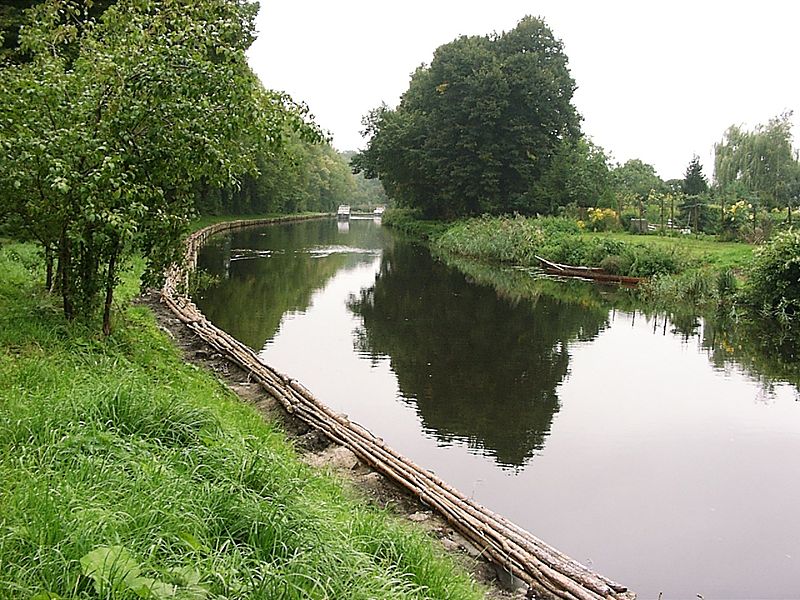

A fascine is a bundle of sticks or brushwood used in construction, generally to strengthen an earthen structure, fill ditches, or make a path acros...
Filled container
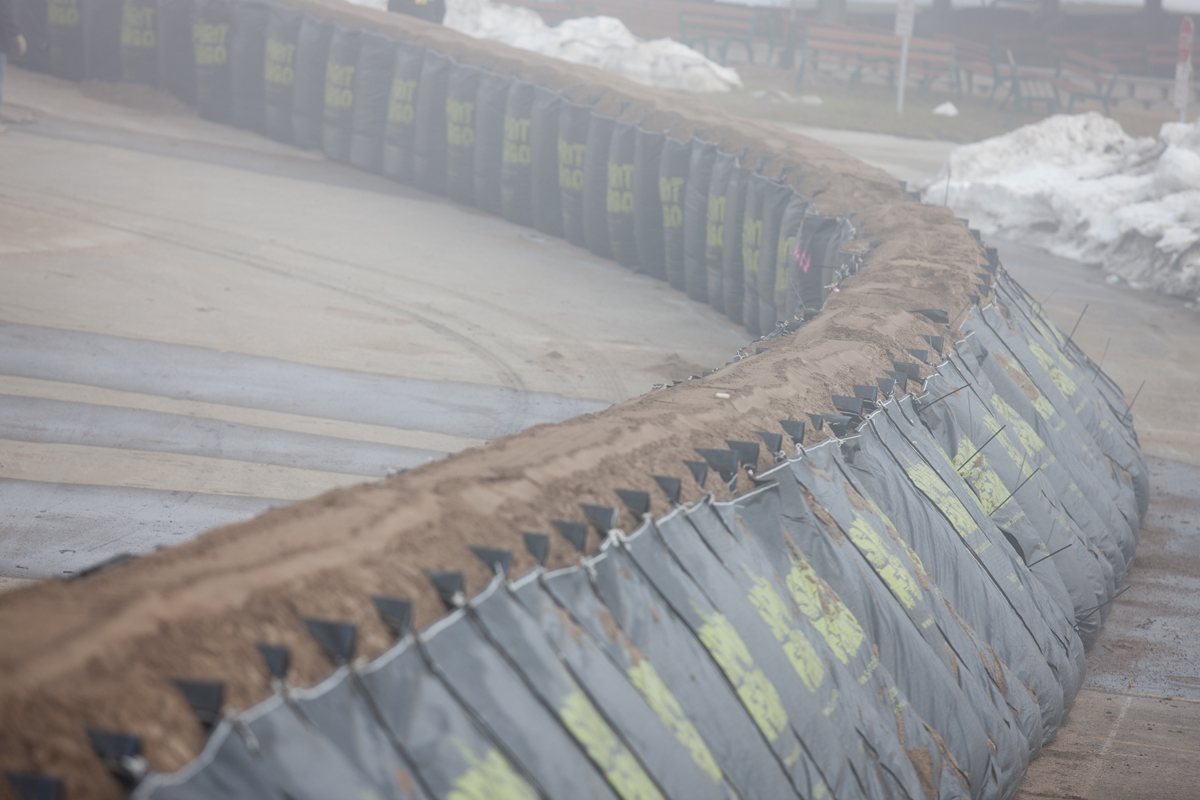

These are cellular barriers filled with aggregates or water to form a barrier against floodwater. Containers can be divided into two categories, pe...
Filter drain
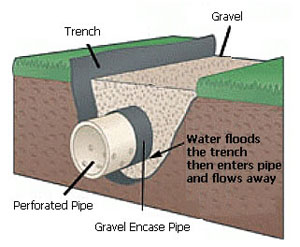
A filter drain is a gravel filled trench, generally with a perforated pipe at the base. Runoff flows slowly through the granular material, trapping...
Filter strip
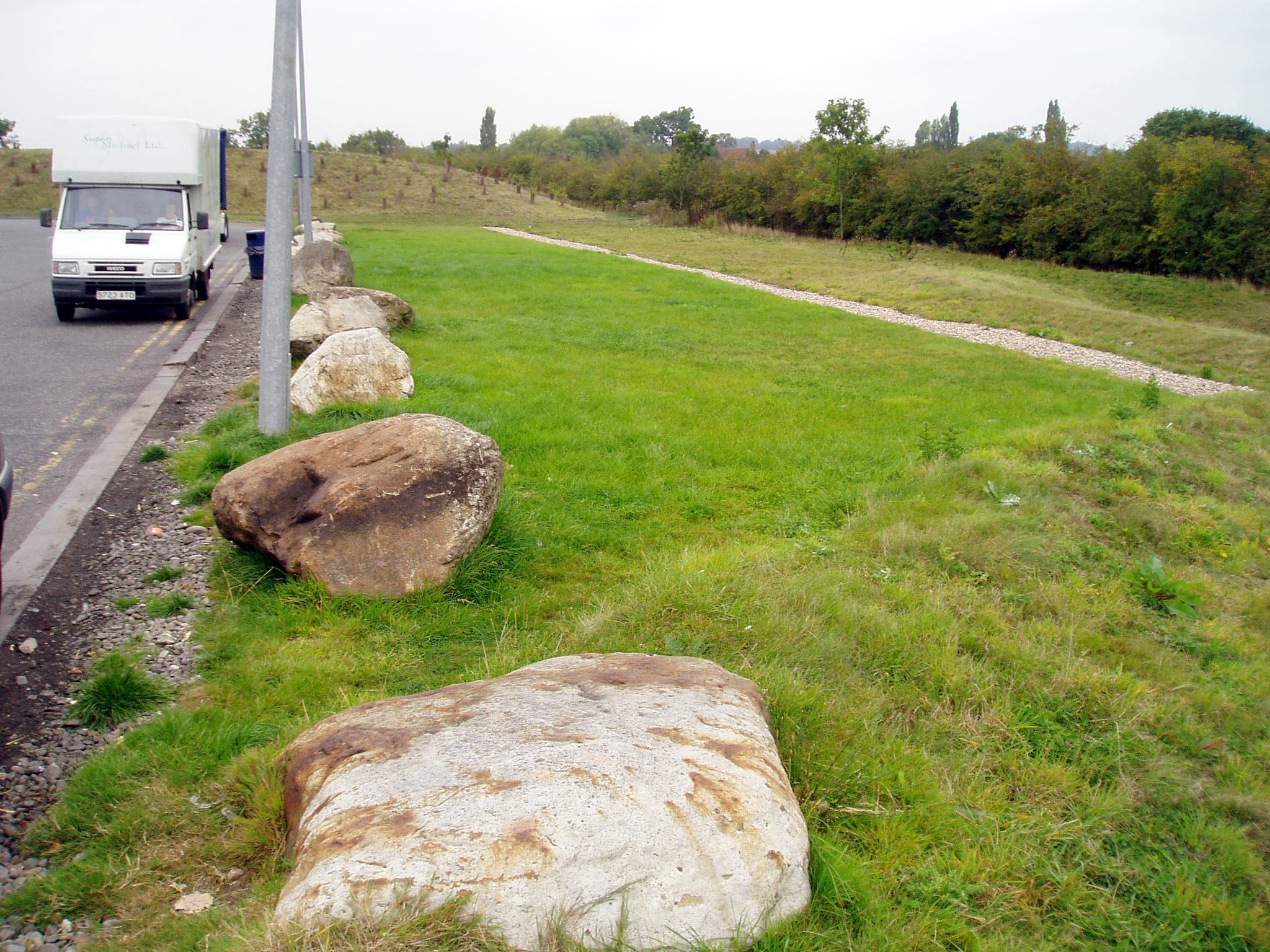

Filter strips are gently sloping, vegetated strips of land that provide opportunities for slow conveyance and infiltration (where appropriate). The...
Filter trench
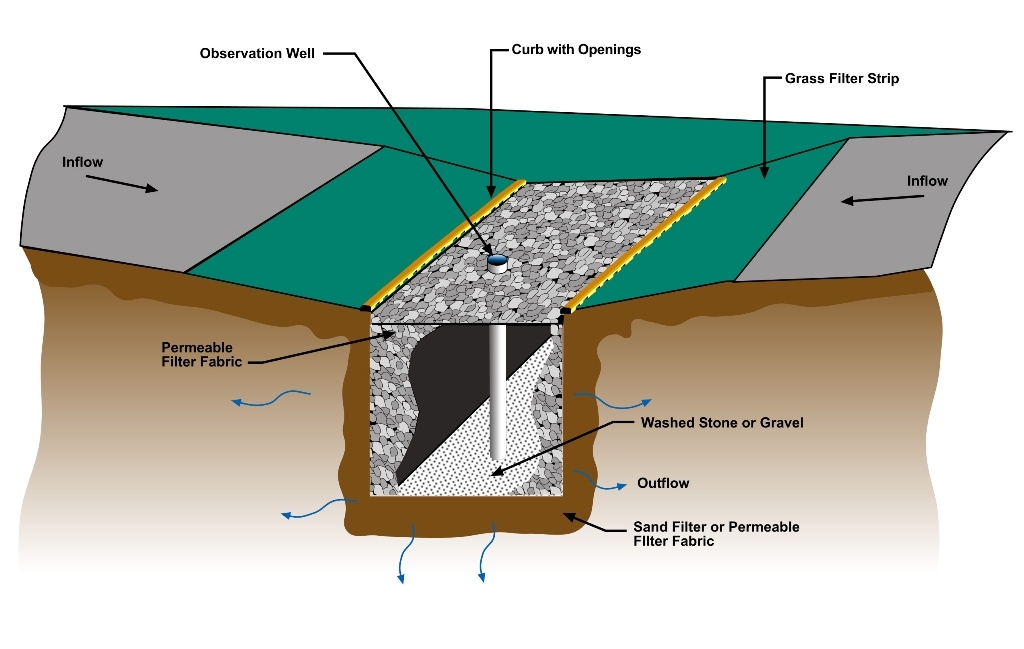
Filter trenches are shallow excavations filled with rubble or stone that create temporary subsurface storage of stormwater runoff. These trenches c...
Flexible water level management
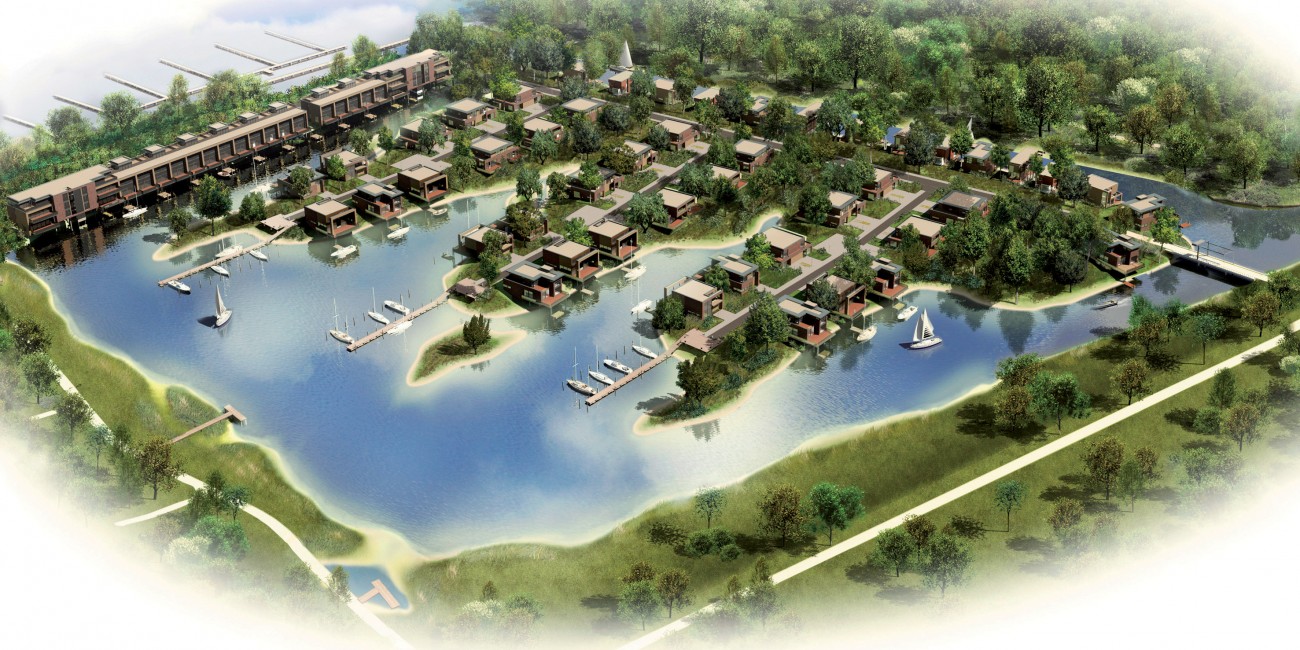

Flexible water level management involves anticipating precipitation that has been forecast. The water level is lowered before a shower is expected,...
Floating agricultural system
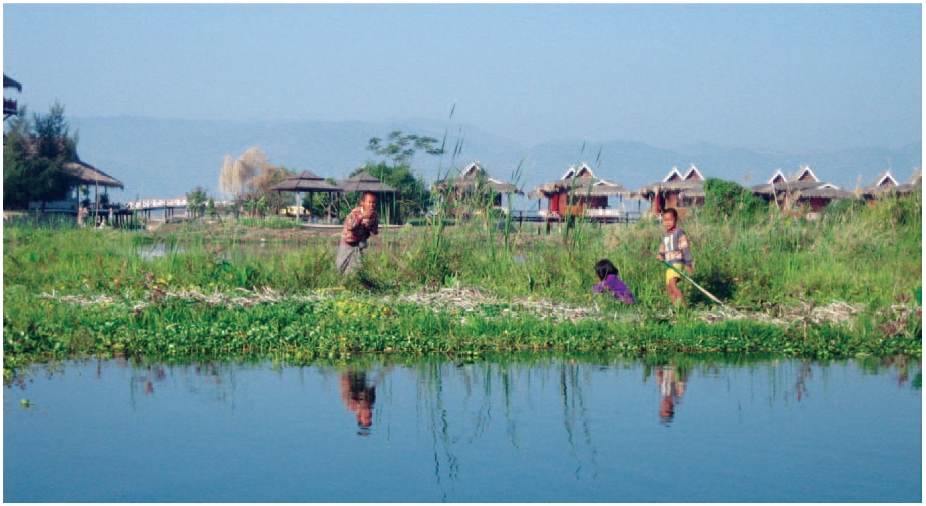

Floating agriculture is a way of utilising areas which are waterlogged for long periods of time in the production of food. The technology is mainly...
Floating building

The basic characteristic of floating buildings is that they are not supported by a firm foundation, but float on water. Traditional foundations are...
Floating road
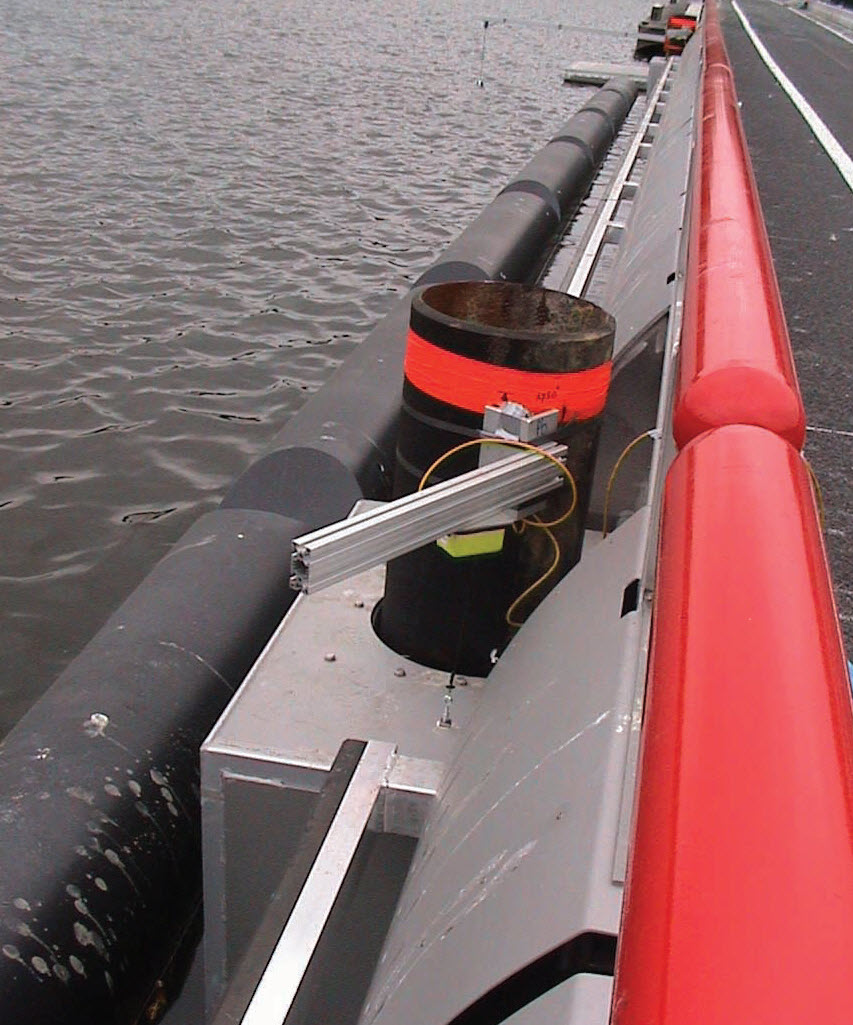

Road transport infrastructure and evacuation routes that are prone to flooding need to be flood proofed to reduce the vulnerability and negative im...
Flood control dam

A flood control dam is a dam built to catch surface runoff and stream water flow in order to regulate the water flow in areas below the dam. Flood ...
Flood detention reservoir
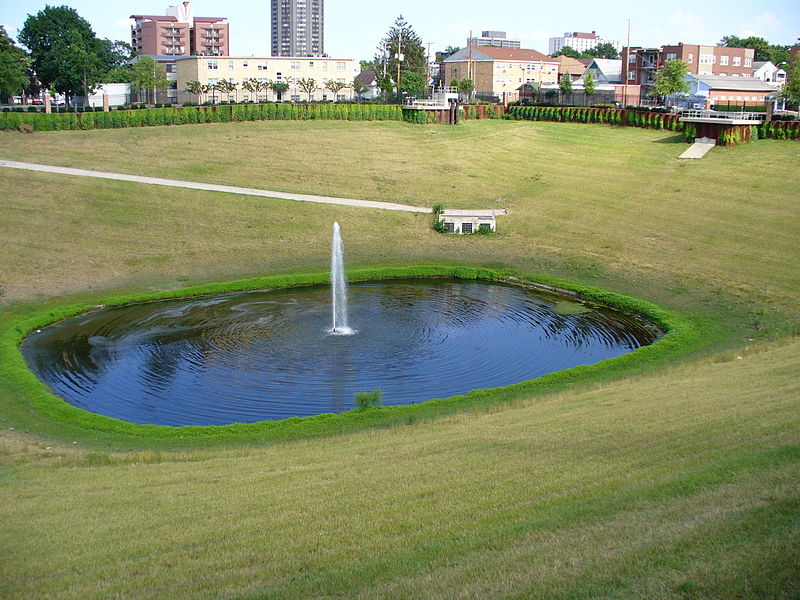

Flood detention reservoir, also known as an attenuation or balancing or flood control reservoir or detention basin, collects water at times of ve...
Flood emergency framework
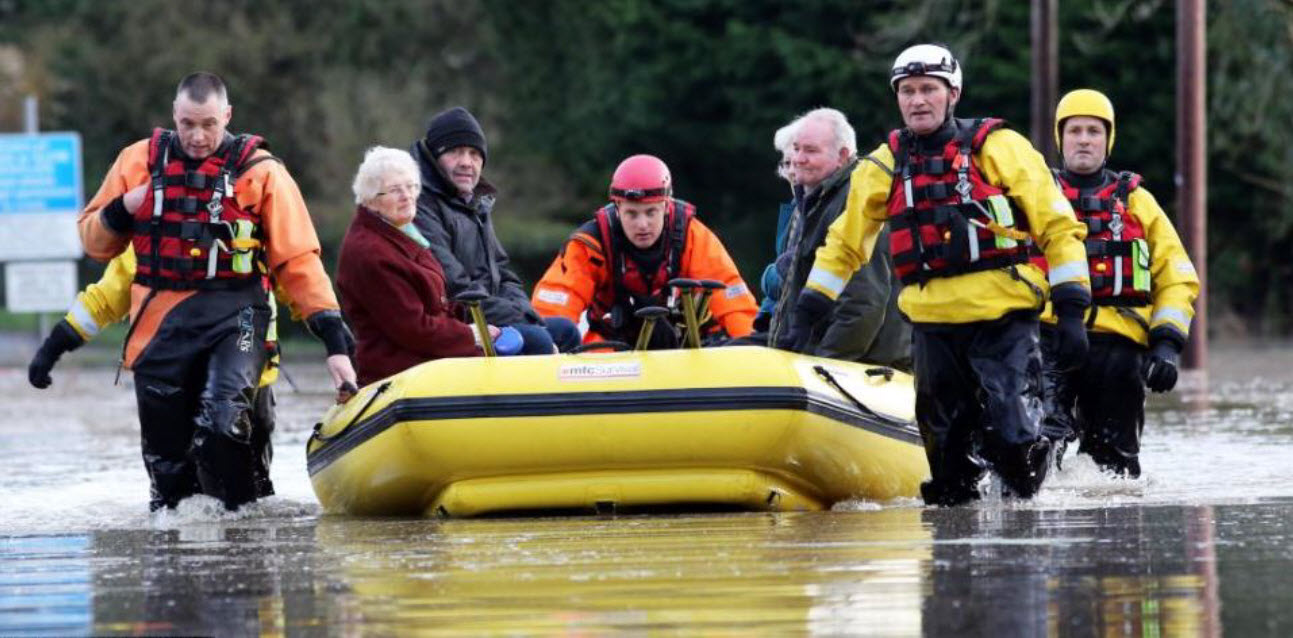

Flood emergency framework sets out the government’s strategic approach to achieving the aims set out below and is intended for use by all those inv...
Flood forecasting and early warning
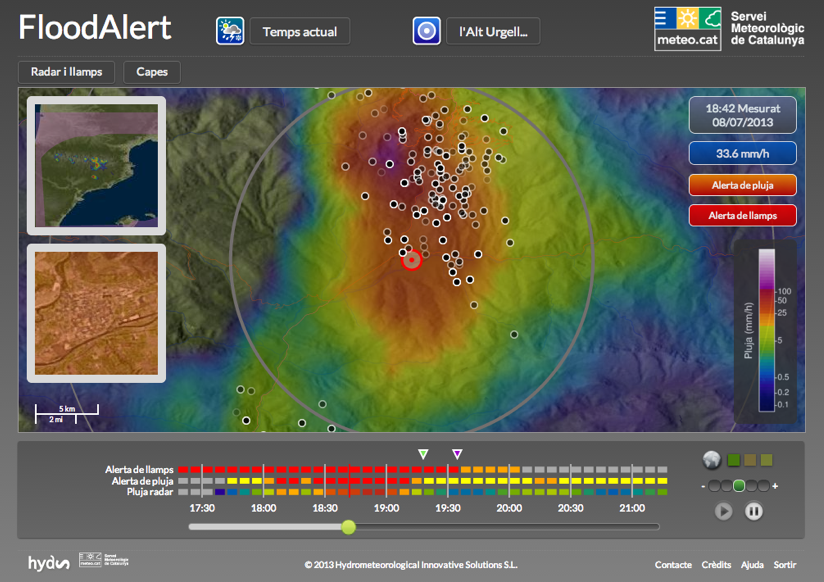
Flood forecasting is an important component of flood warning. Flood forecasting involves prediction of water levels and flows at particular locatio...
Flood gate
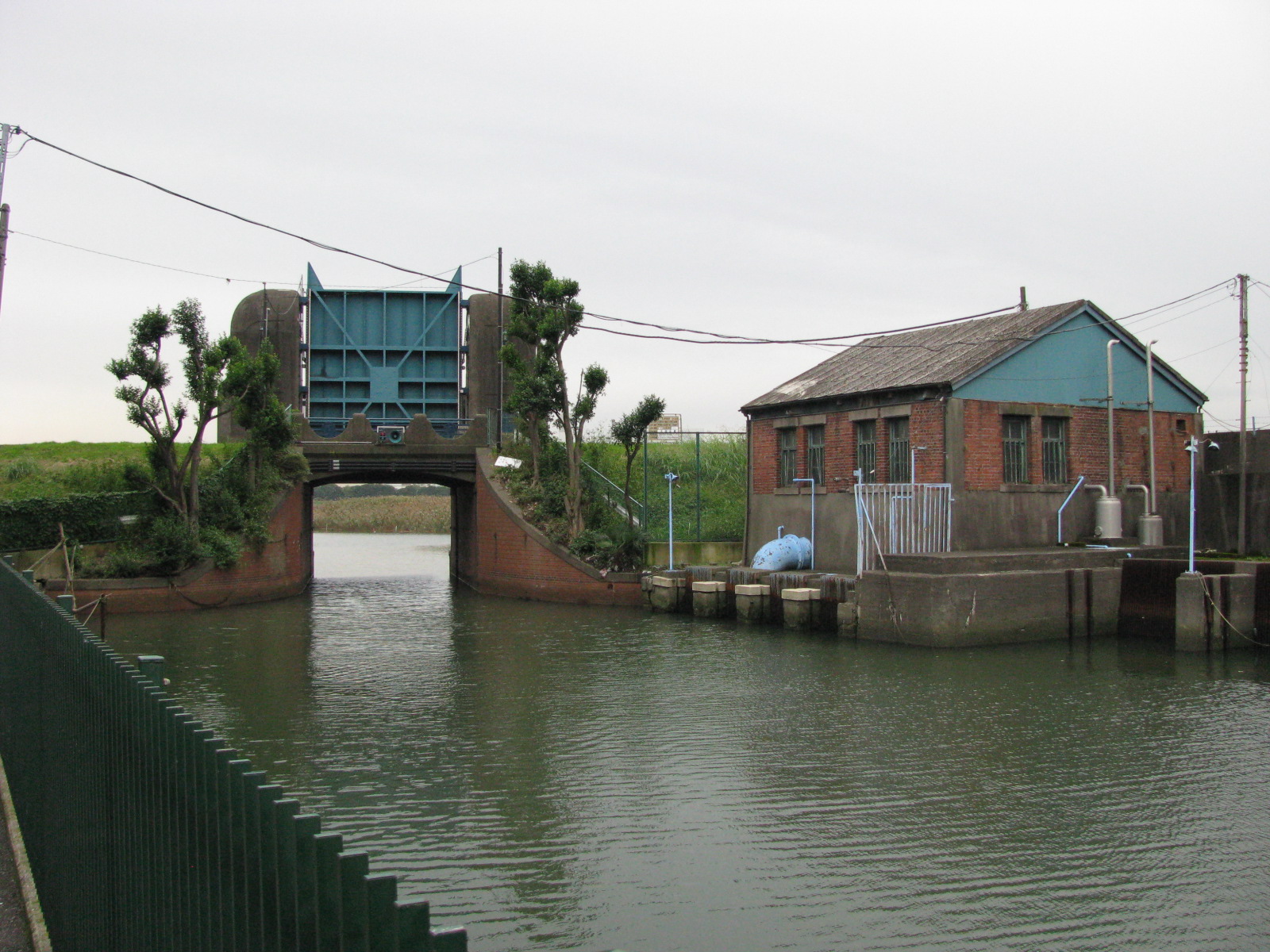

These barriers are made of a single or pair of rigid sections (usually steel or fibreglass), designed to close a gap within a flood defence. They a...
Flood hazard mapping
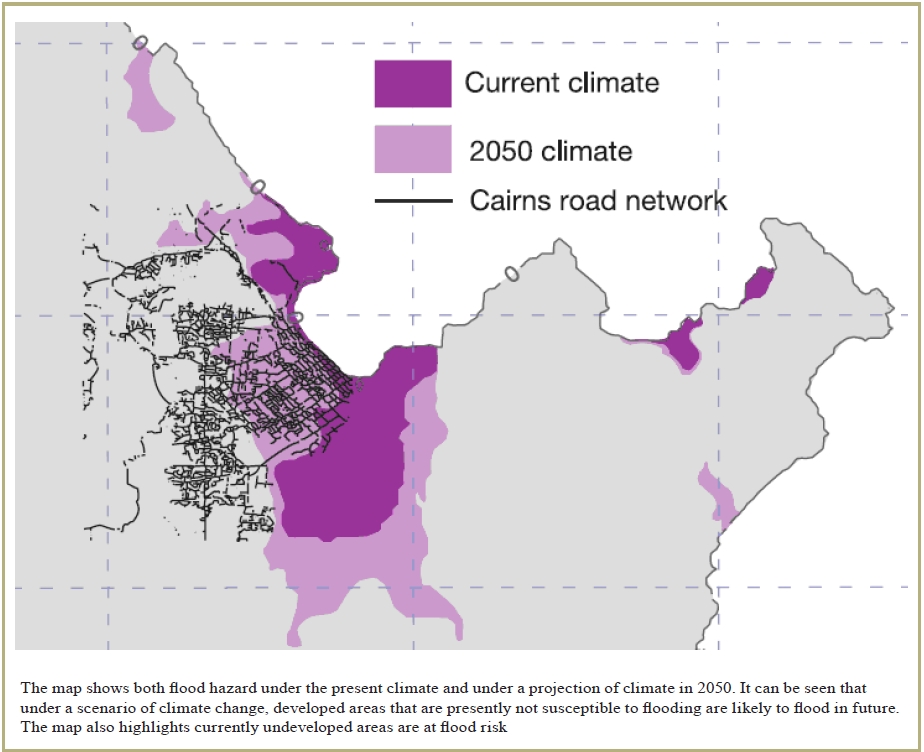
Flood hazard mapping is an exercise to define those areas which are at risk of flooding under extreme conditions. As such, its primary objective is...
Flood insurance

Flood insurance is an important risk management tool that can be applied at various levels: individual, corporate and government. It provides a mec...
Floodplain excavation
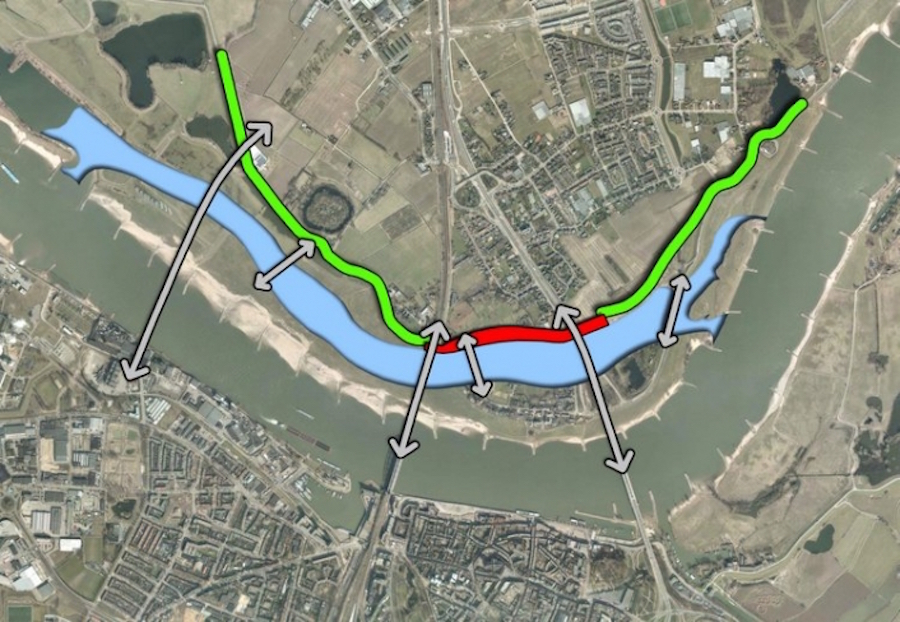
Floodplain excavation is a measure by which gradual height increase caused by sedimentation on flood plains may be counteracted. The floodplain can...
Flood proof infrastructure
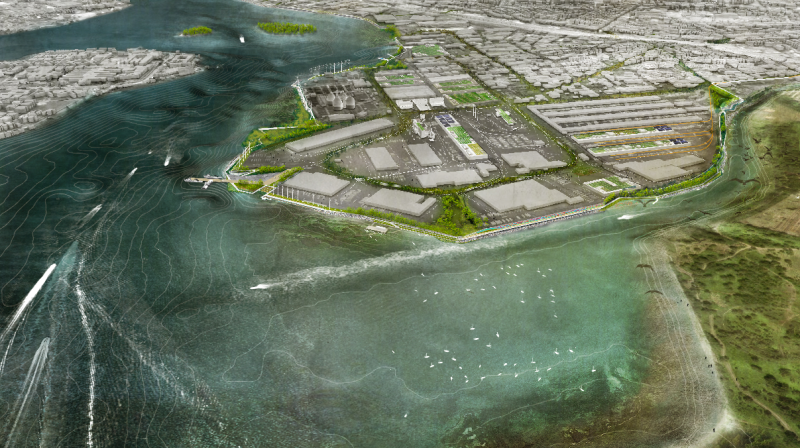

Evacuation routes and infrastructure in cities that are prone to flooding need to be flood proofed. Available options to reduce the negative impact...
Flood shelter

Flood shelters are created in areas which experience severe flooding. Elevated flood shelters should be constructed above the highest expected floo...
Floodwall
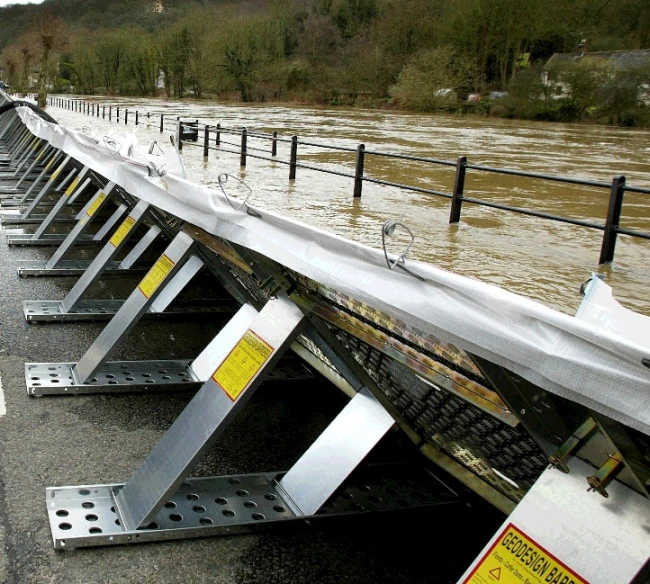

A floodwall is a primarily vertical artificial barrier designed to temporarily contain the water of a river or other waterway which may rise to unu...
Frame barrier

Frame barriers consist of rigid frames with impermeable membranes or sections spanning between them. They rely on supporting frames and the weight ...
Freestanding barrier
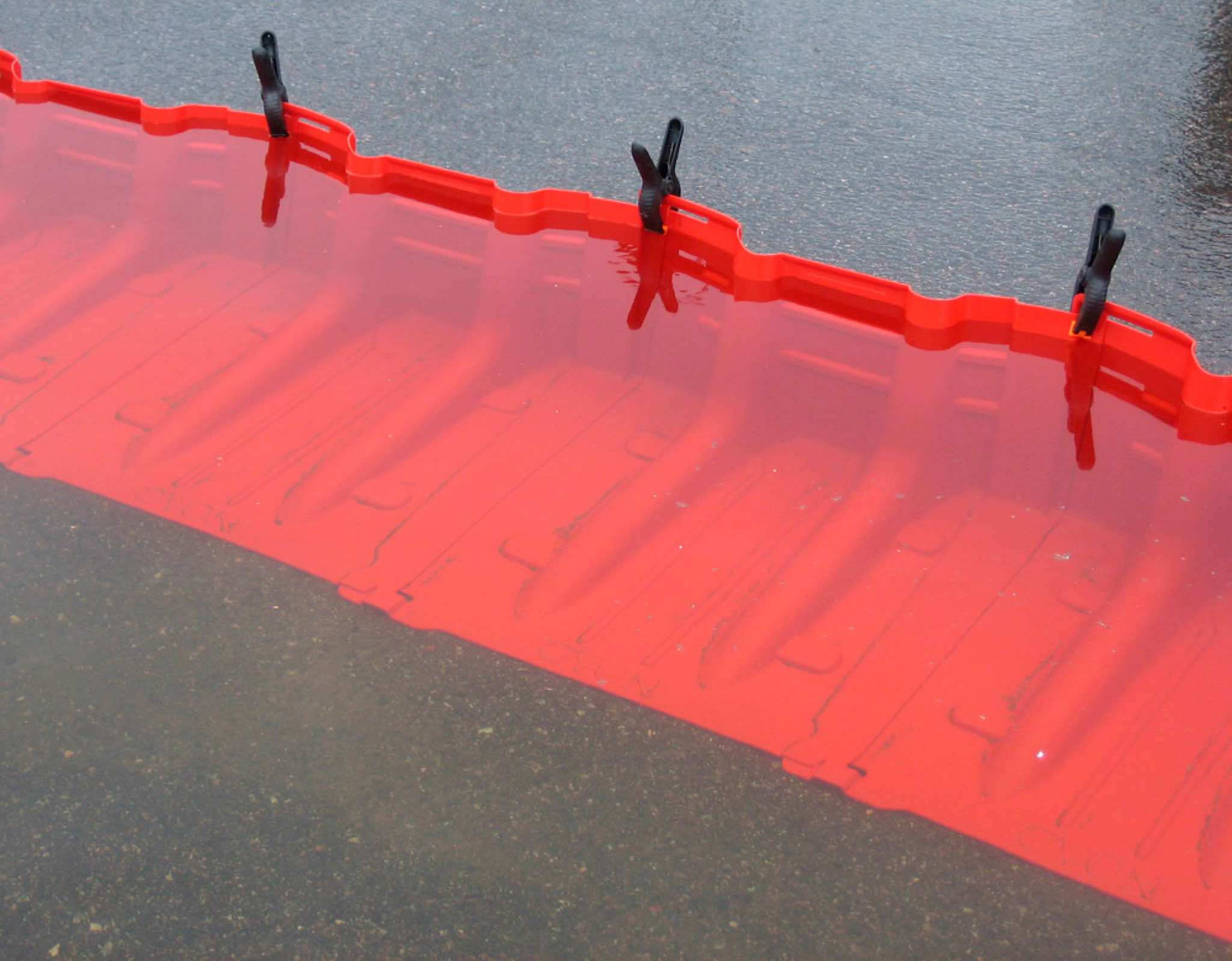

These modular systems are made of impermeable materials and are joined together to form a continuous barrier or wall. These products are self suppo...
Government debt instrument

A common way for emerging-economy governments to raise funds after a disaster is to borrow from their central bank reserves or to issue government ...
Grated channels
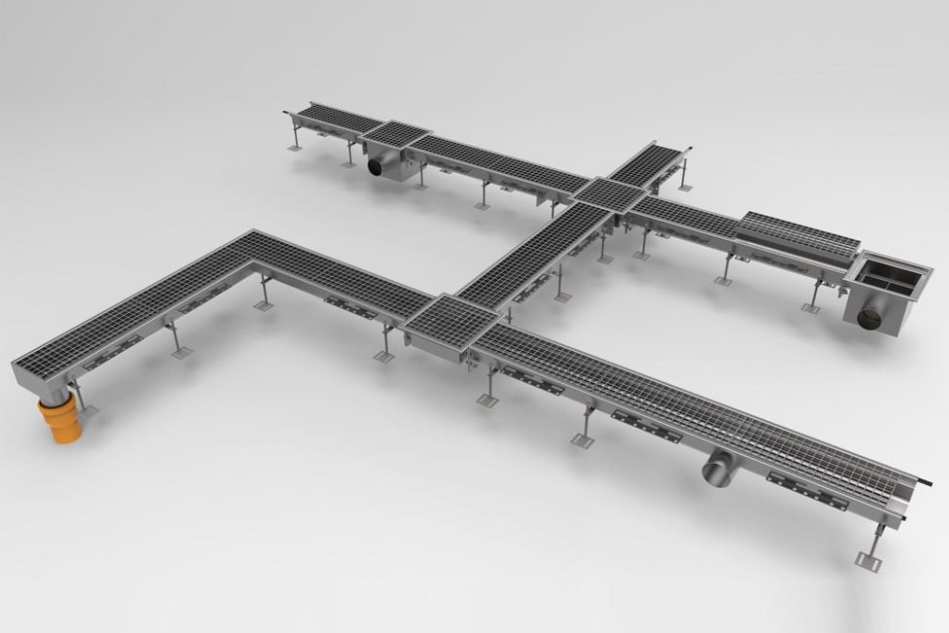
Grated channels collects water at the side of the road and can channel water in storm drains into the harbour.
Green roof
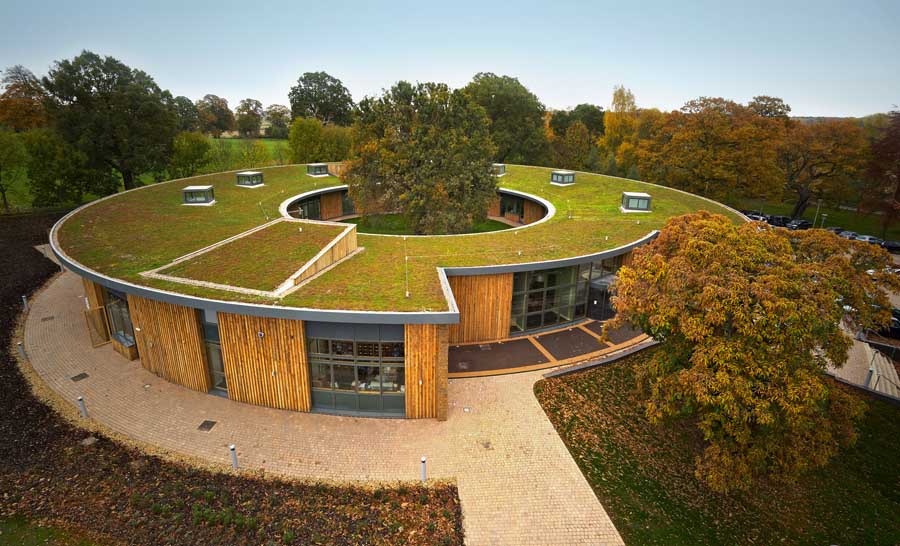

Green roof belongs in the category of SUstainable Drainage Systems (SUDS) and aims at source controlling. A green roof or living roof is a roof of ...
Green wall
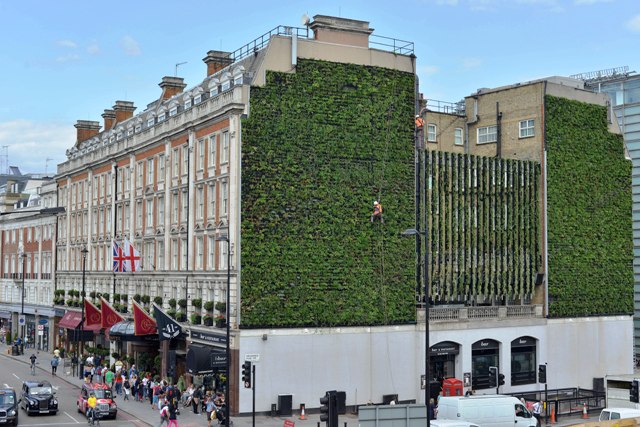

A green wall is a wall partially or completely covered with vegetation that includes a growing medium, such as soil. Most green walls also feature ...
Groyne
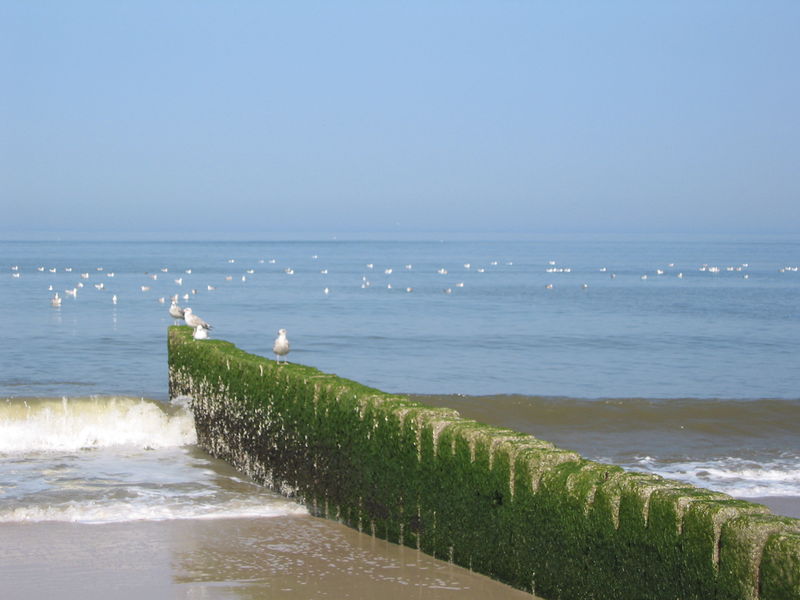

A groyne is normally a straight structure perpendicular to the shoreline. Groynes work by blocking (part of) the littoral drift, whereby they trap/...
Gutter
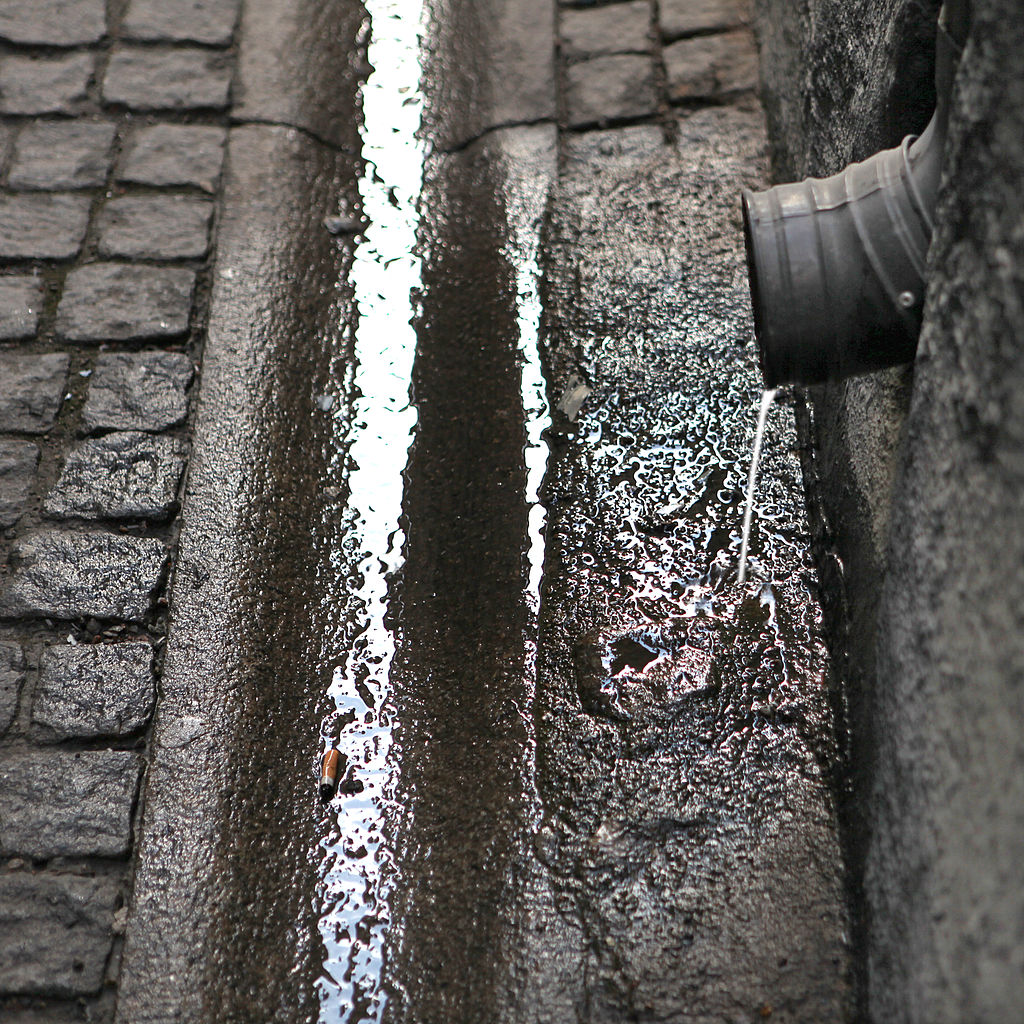

A gutter is a non-permeable open drain to collect transport rainwater. Usually a gutter runs along a road. It is connected to either a manhole or a...
High water mark

A high water flood mark is a point that represents the maximum rise of a body of water over land. Such a mark is often the result of a flood and ai...
Hydraulic filling

Hydraulic Fill is fill in which the materials are deposited by a flowing stream of water. This fill material will originate from a borrow area or d...
Hydrological and Meteorological Observatory

Hydrological and Meteorological Observatory is an observation service dedicated to long-term monitoring of climatological and hydrological changes....
Improved construction site preparation

Improved construction site preparation is focused on improving the strength and drainage capabilities of an area that is converted from a rural or ...
Increased capacity of sewer/drainage system

Increasing the capacity of the sewer/drainage system increases the ability of the system to drain excess surface water during heavy rains and preve...
Increase of infiltration capacity
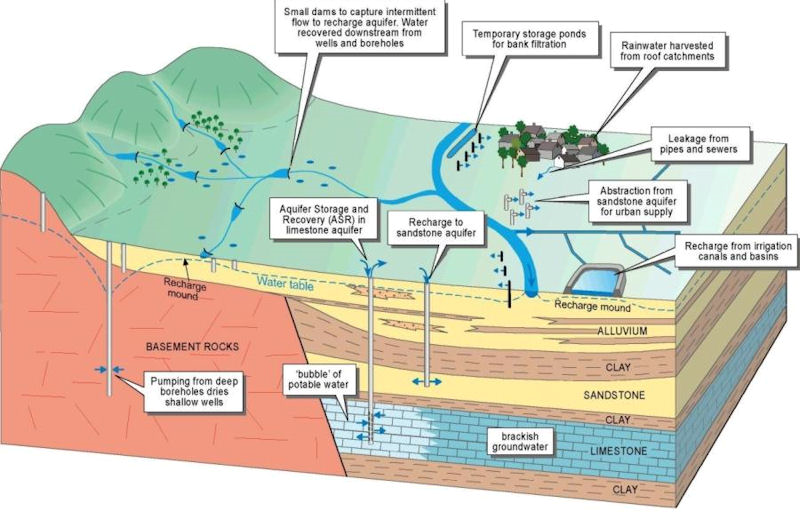
Improving the soil infiltration capacity means improving the permeability of the soil. If the infiltration capacity of the soil is increased, more ...
Independent commission for flood and disaster risk reduction

An Independent commission is a politically independent executive arm. It is alone responsible for drawing up proposals for new legislation. (Europe...
International loan

Emerging-economy governments have the opportunity to borrow at low interest rates from international lending organizations aiming at pre-disaster p...
Land claim
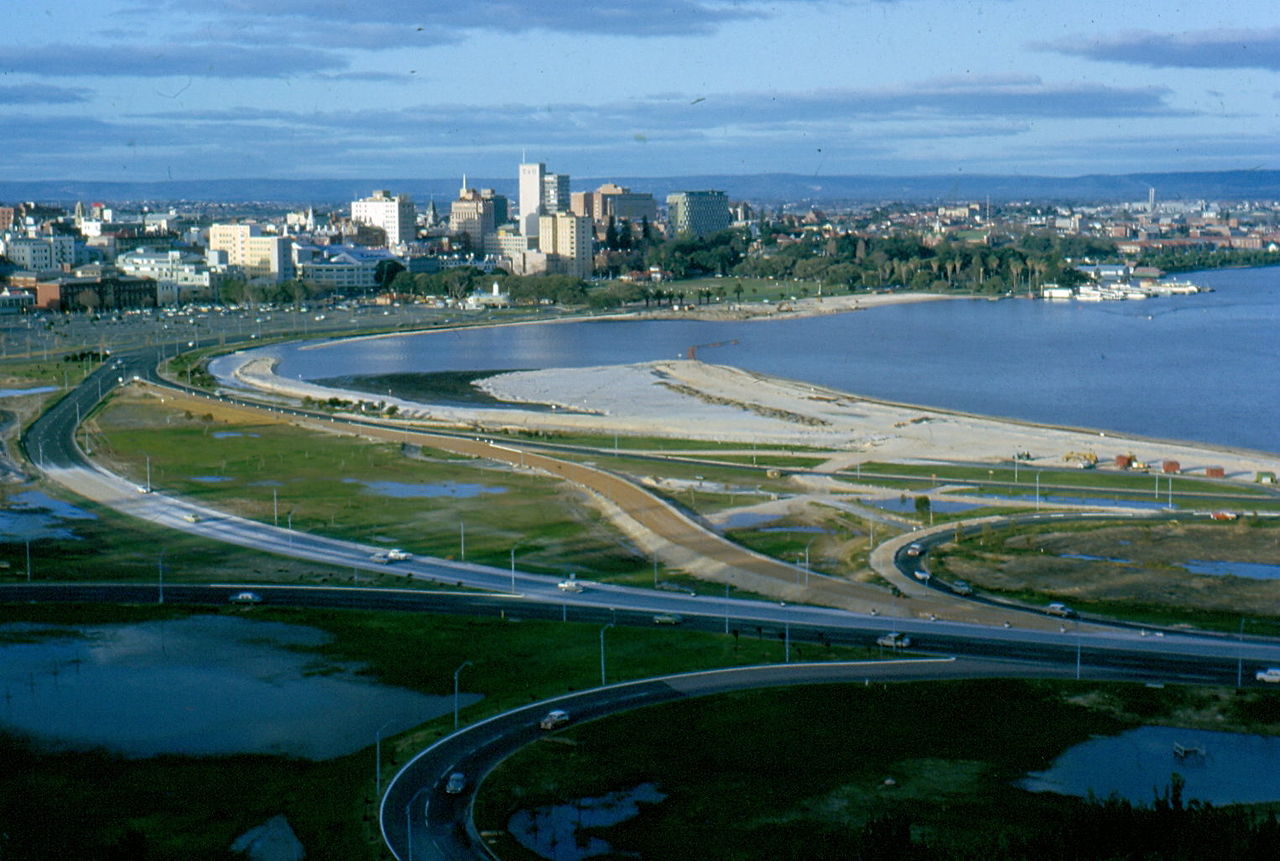

The main objective of land claim is neither erosion nor storm reduction. The aim of land claim is instead, to create new land from areas that were ...
Land use plan / spatial planning
Spatial planning systems are the methods used by the public sector to influence the distribution of people and activities in spaces of various scal...
Limassol Drainage Master Plan

Storm-Water, Drainage Master Plan was prepared by SBLA in 1992. In 2003 it was updated. About 60% has been implemented.
Living with water - principles
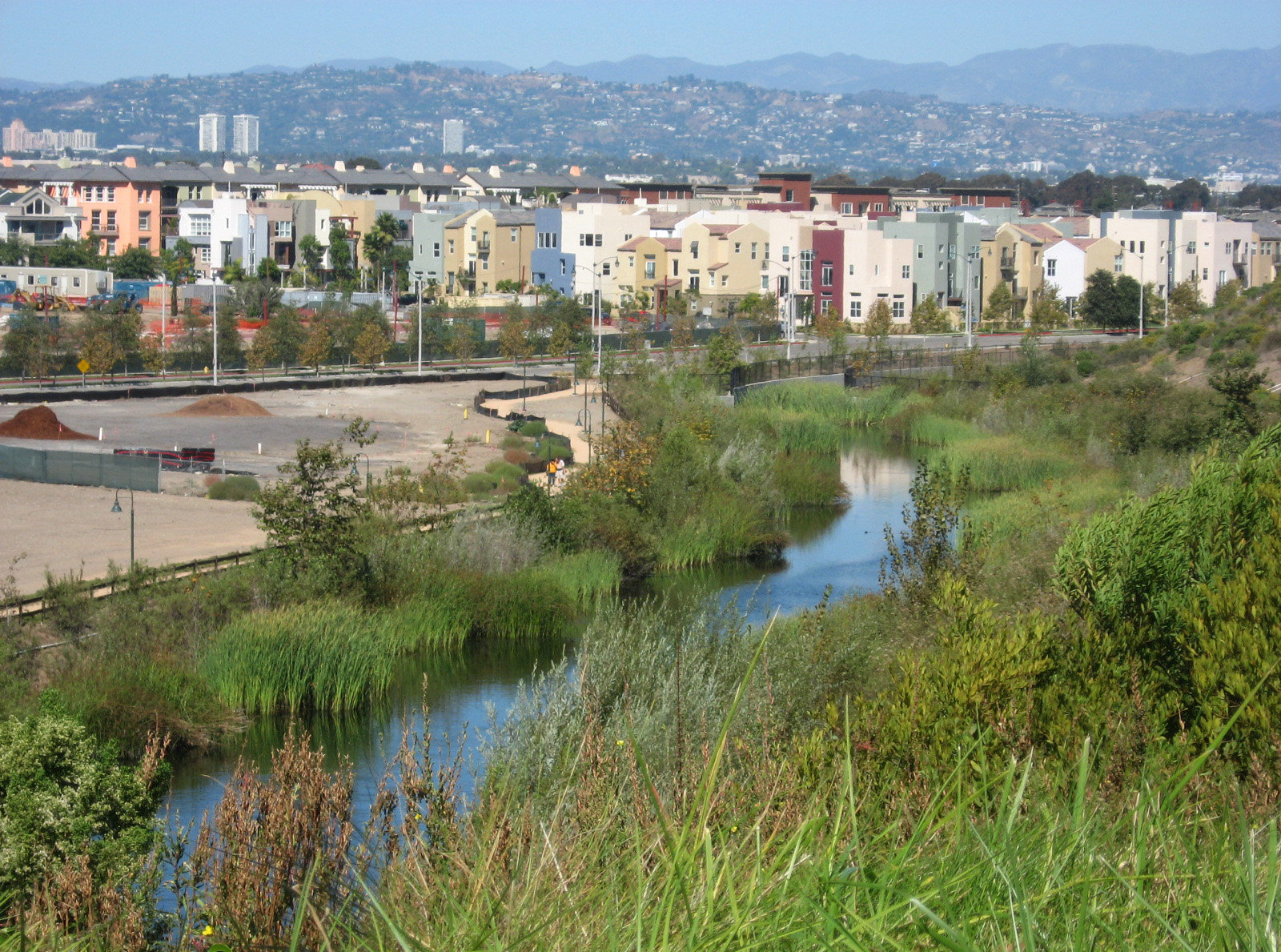

The pursuit of a safe, healthy and sustainable water management is of national interest in the Netherlands. Themes like "water and the city", "wat...
Maintenance of hydraulic structures of the storm drainage system

Set up regulations on maintenance of the hydraulic structures and drainage network infrastructures so that their maximum conveyance capacity will b...
Managed realignment
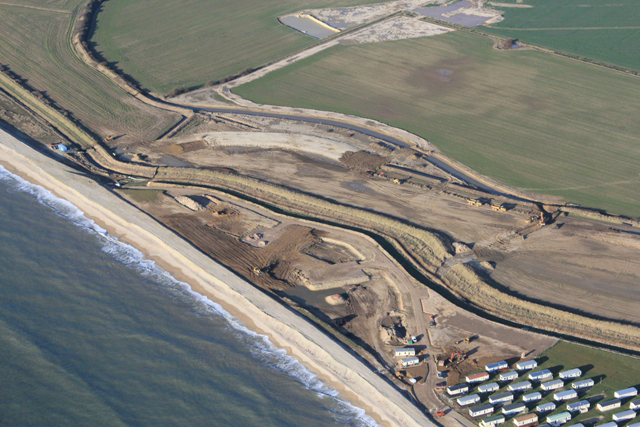

Managed realignment or managed retreat allows an area that was not previously exposed to flooding by the sea to become flooded by removing coastal ...
Monitoring and flood forecasting through partnerships

Organizing and recording partnerships between the various actors so that optimal responsiveness of the population can be produced in case of a warn...
Multi-functional flood defences

Multifunctional Flood Defences (MFD) is a newly developed concept to optimize allocation of urban space rather than constructing stand-alone struct...
Multi-layer safety as a central concept for flood protection
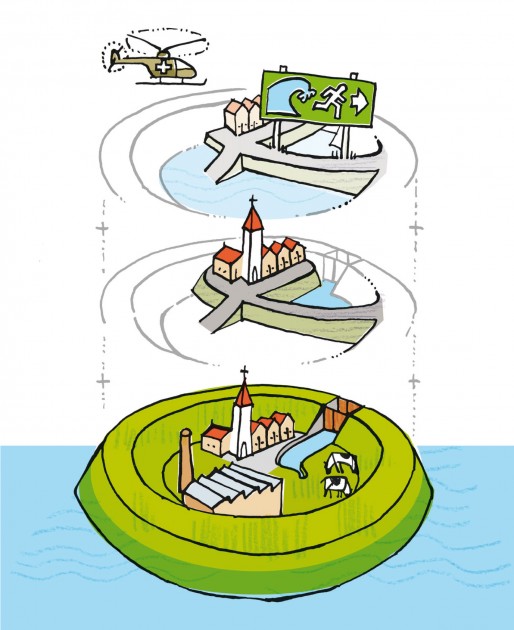
The central concept for the revised water safety policy is formed by 'multi-layer safety'. In this concept safety is assured through multiple layer...
Multi-level capacity building

According to the UNDP, in the global context, capacity refers to the ability of individuals and institutions to make and implement decisions and pe...
Municipal flood control plan

The municipal plan expresses the shared goals, objectives and priorities of a community and allows its members to work together for a specific goal...
Network of waterways
Ένα δίκτυο εσωτερικής ναυσιπλοΐας εστιάζει κυρίως στη διασύνδεση των υδάτινων σωμάτων που βρίσκονται σε κοντινές αποστάσεις. Συνδέοντάς τα, με υπόγ...
Permeable paving
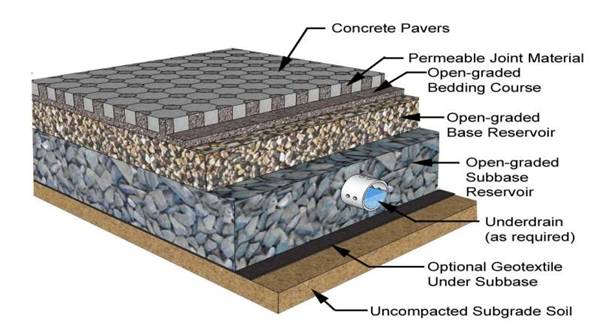
Permeable paving is a range of sustainable materials and techniques for permeable pavements with a base and sub base that allow the movement of wat...
Polder
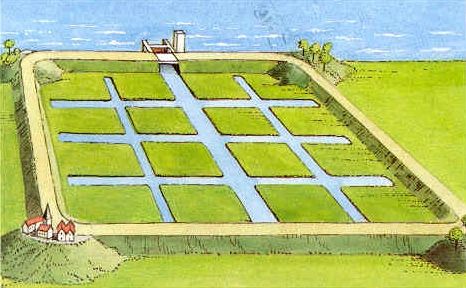
A polder is a low-lying tract of land enclosed by embankments (barriers) known as dikes that forms an artificial hydrological entity, meaning it ha...
Pond
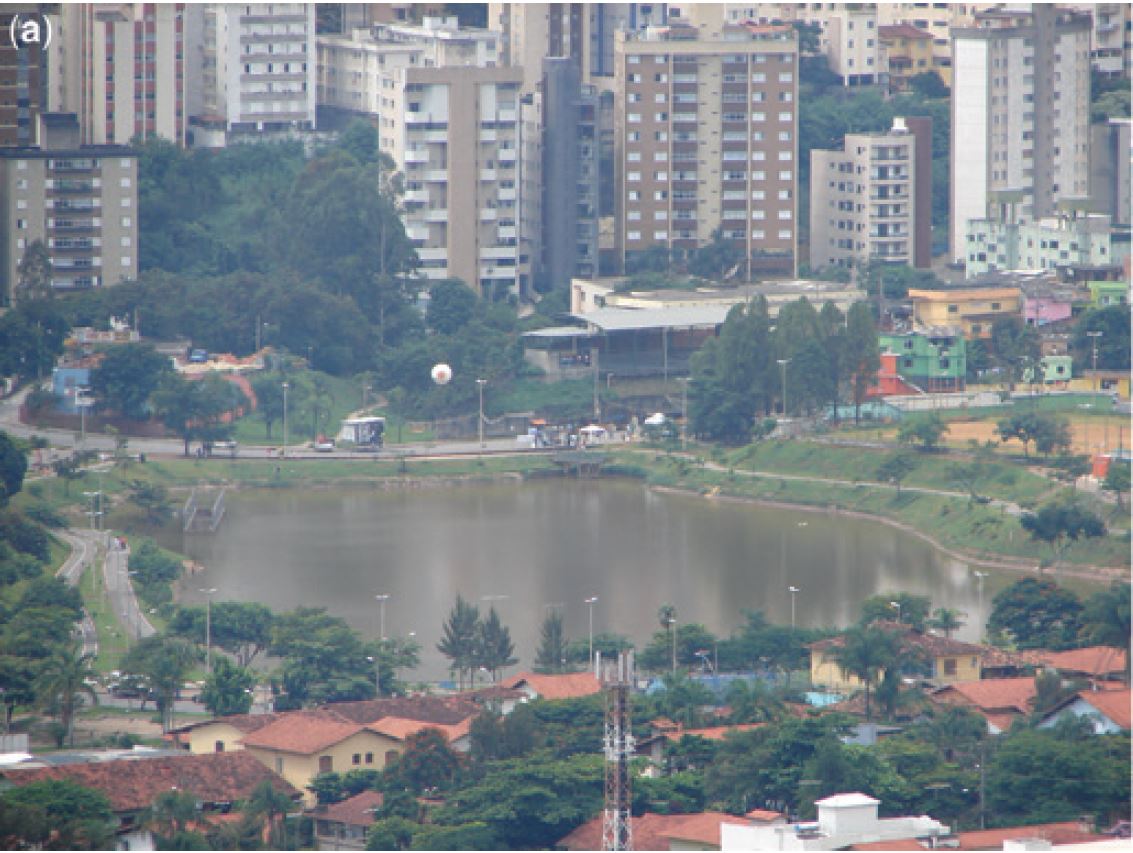

A pond is a body of standing water, either natural or artificial, that is usually smaller than a lake. They may arise naturally in floodplains as p...
Port restructuring
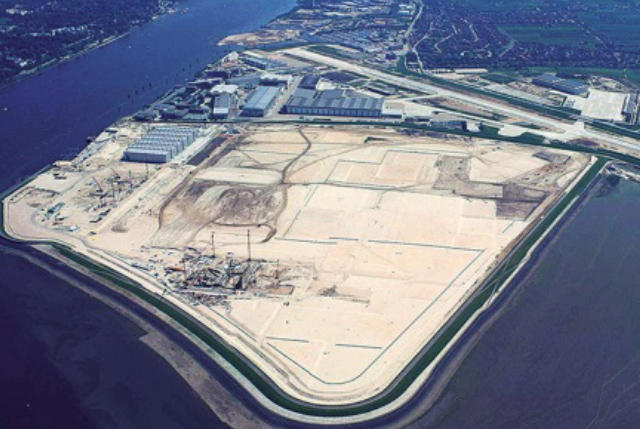

Restructuring of the layout of the port, its equipment and flood protection system.
Prescription on the construction code
Impose implementation of measures for mitigation and vulnerability reduction through the construction code of town planning. (ASFPM, Modifications ...
Public awareness, information, education and communication

Inform local citizens and visitors about the major hazards through public meetings, flyers, website, training, collaborative platforms, brochures,...
Pumping station
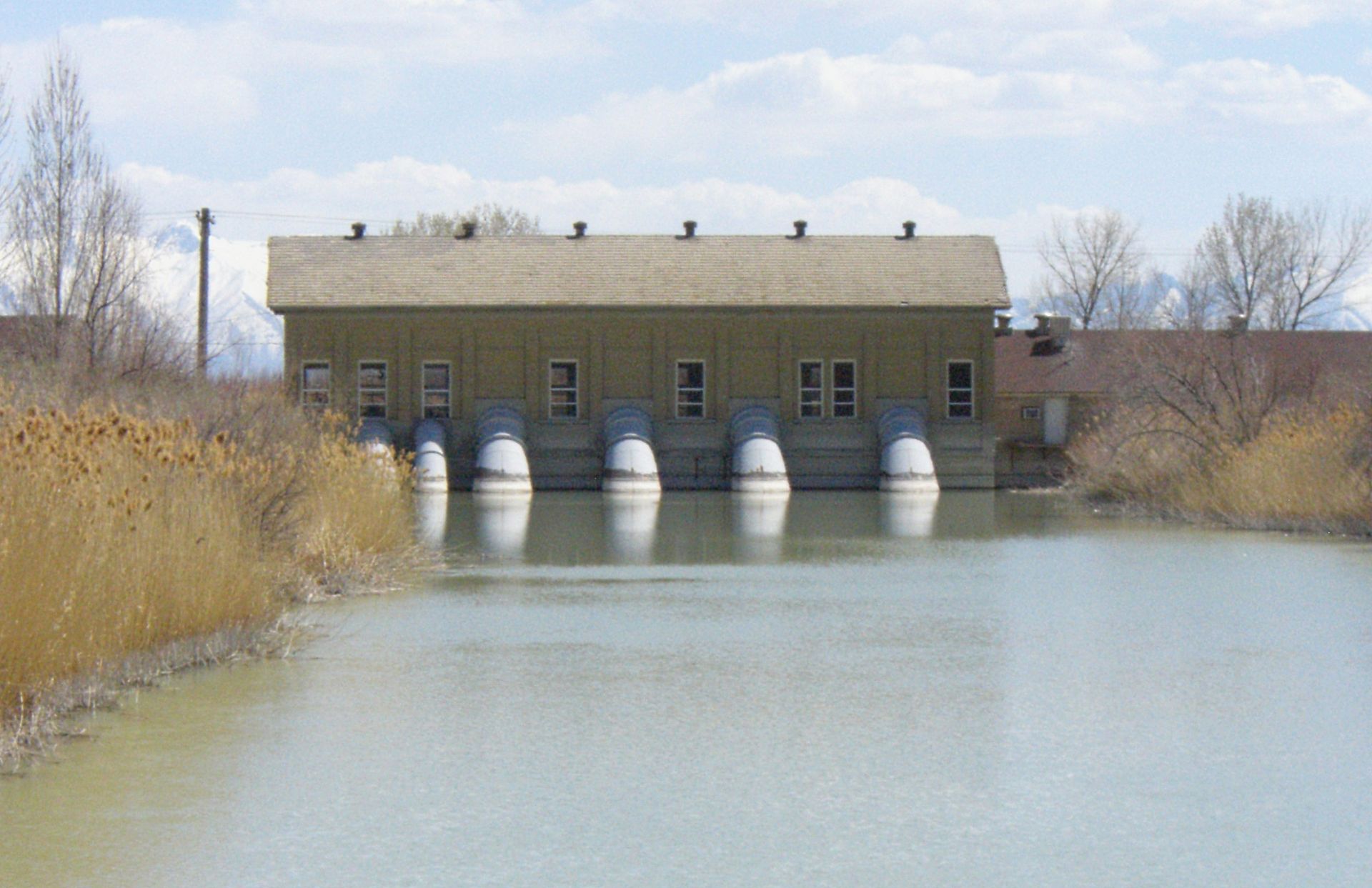

A pumping station is used to discharge water out of an area. It can be used to transport sewer water in pressure mains. Another option is to be use...
Rain garden
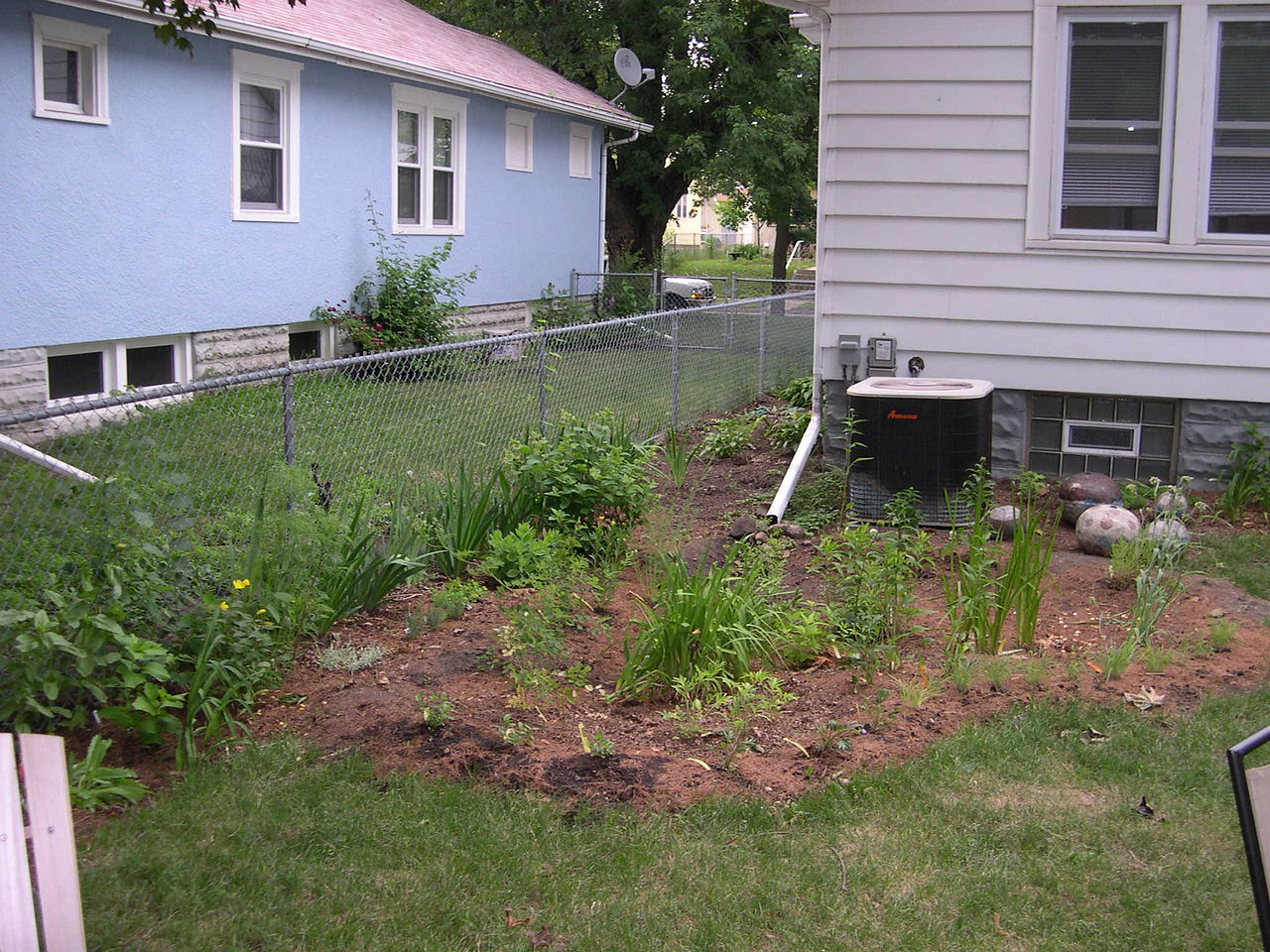

A rain garden is a planted depression or a hole that allows rainwater runoff from impervious urban areas, like roofs, driveways, walkways, parking ...
Rainwater disconnection
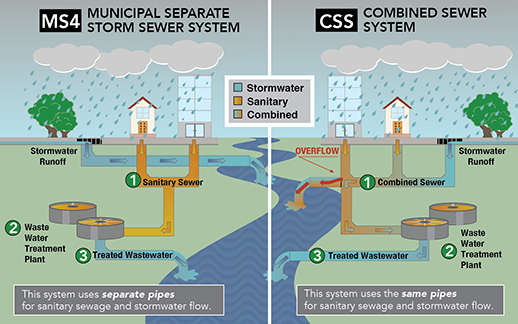
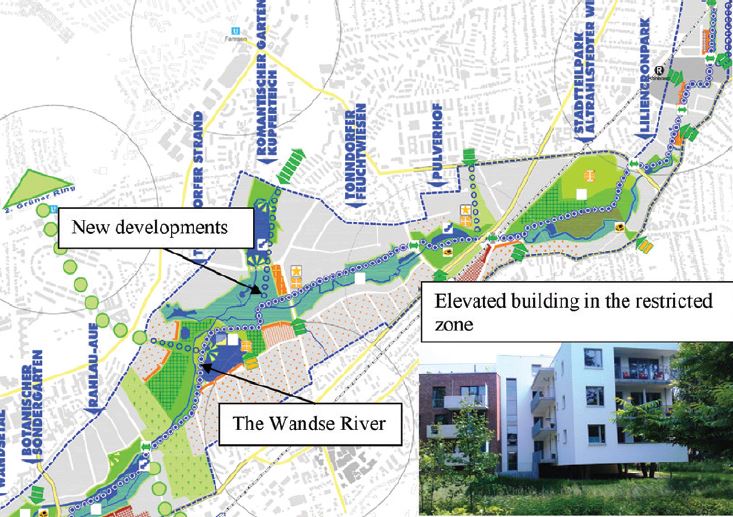
Rainwater disconnection, i.e. the separation of the sewage system from the rainwater discharge system, is also a solution to prevent sewer flooding...
Rainwater harvesting system
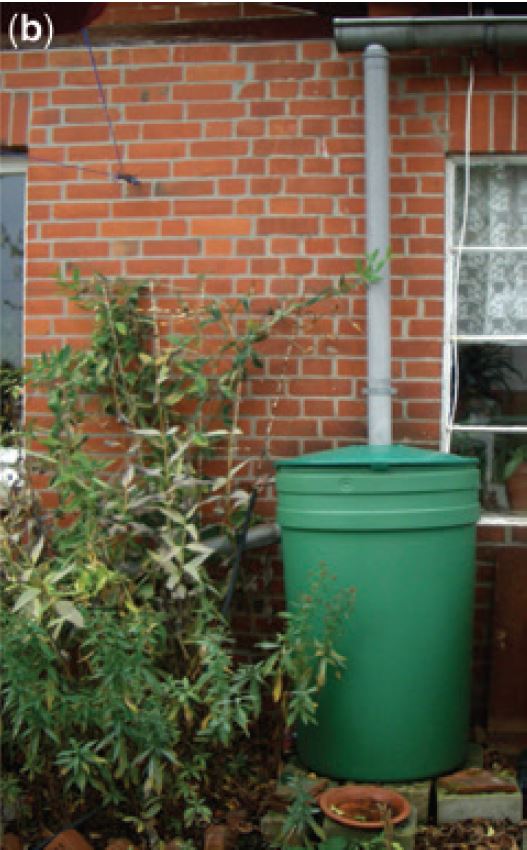

The term rainwater harvesting refers to reuse of stored water, including water purification, and can form part of a sustainable drainage system. Al...
Rainwater storage beneath sports fields
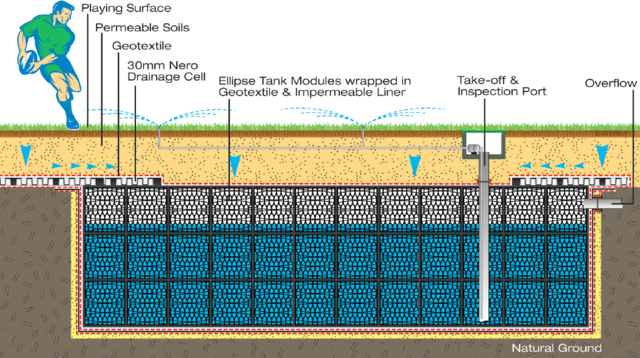
One option for creating additional water storage facilities is storing in underground crates. This is a hidden technology that fits the criteria of...
Raised kerb
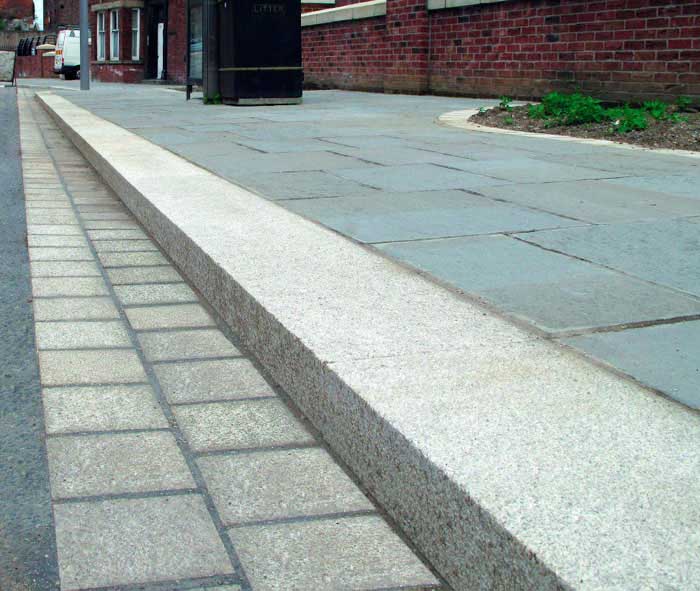

Kerb or curb is the edge of the pavement at the side of the road. Water can be channeled along streets with raised kerbs and also to limit contact ...
Red alert exercise
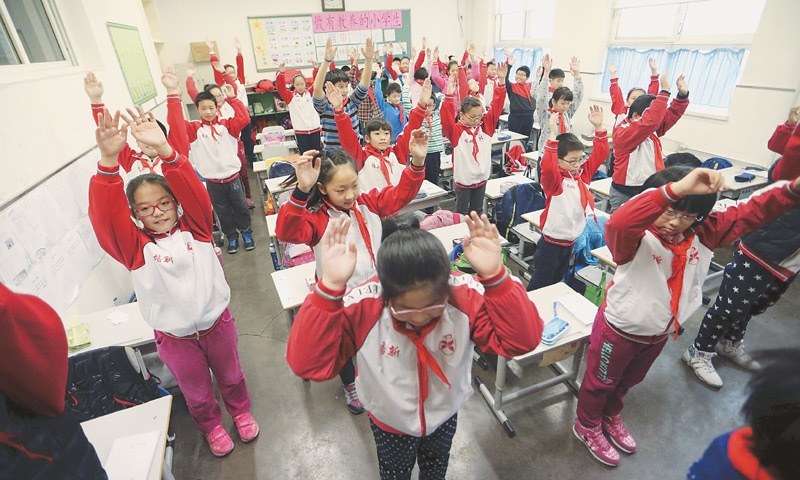

A red alert emergency exercise enables the simulation/testing of population/authorities response and plans in case of an extreme flood event occurs...
Rescue plan
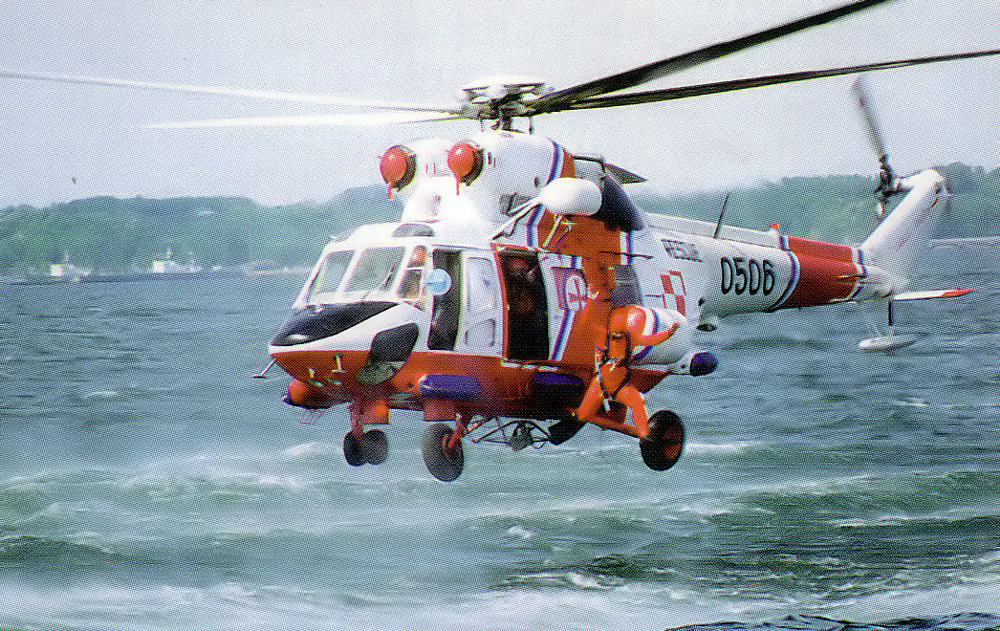

The aim of flood rescue operations is to move people from immediate or potential harm to safety. Failed evacuation operations (e.g. evacuation oper...
Reserve funds

Building a catastrophic reserve fund is one of the measures assisting risk management as it will enable claims to be provided in years with unusual...
Retention of rainwater in the vicinity of a roundabout
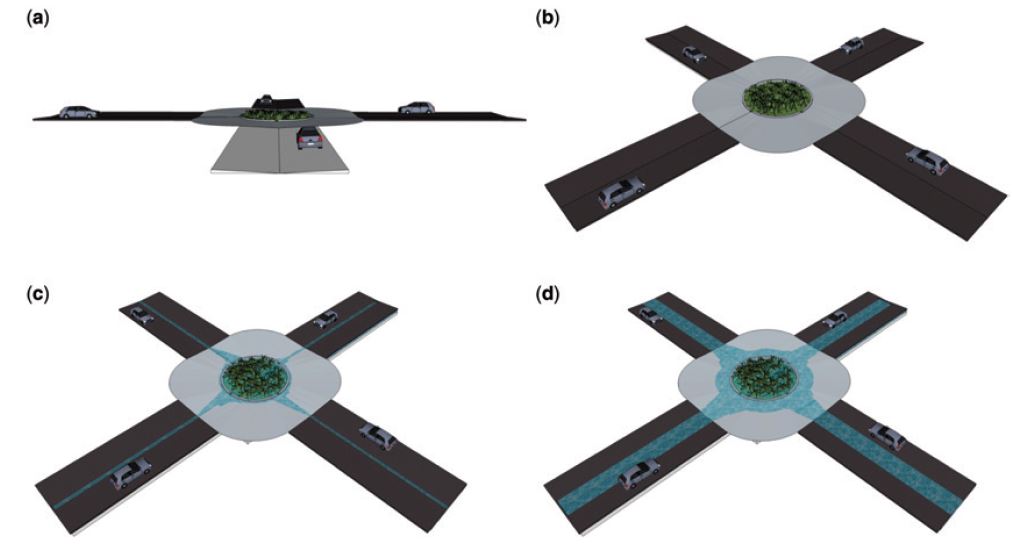
In case of an extreme event the surface runoff is conveyed by the streets to a roundabout, where it is temporarily stored and infiltrated into the ...
Revetment
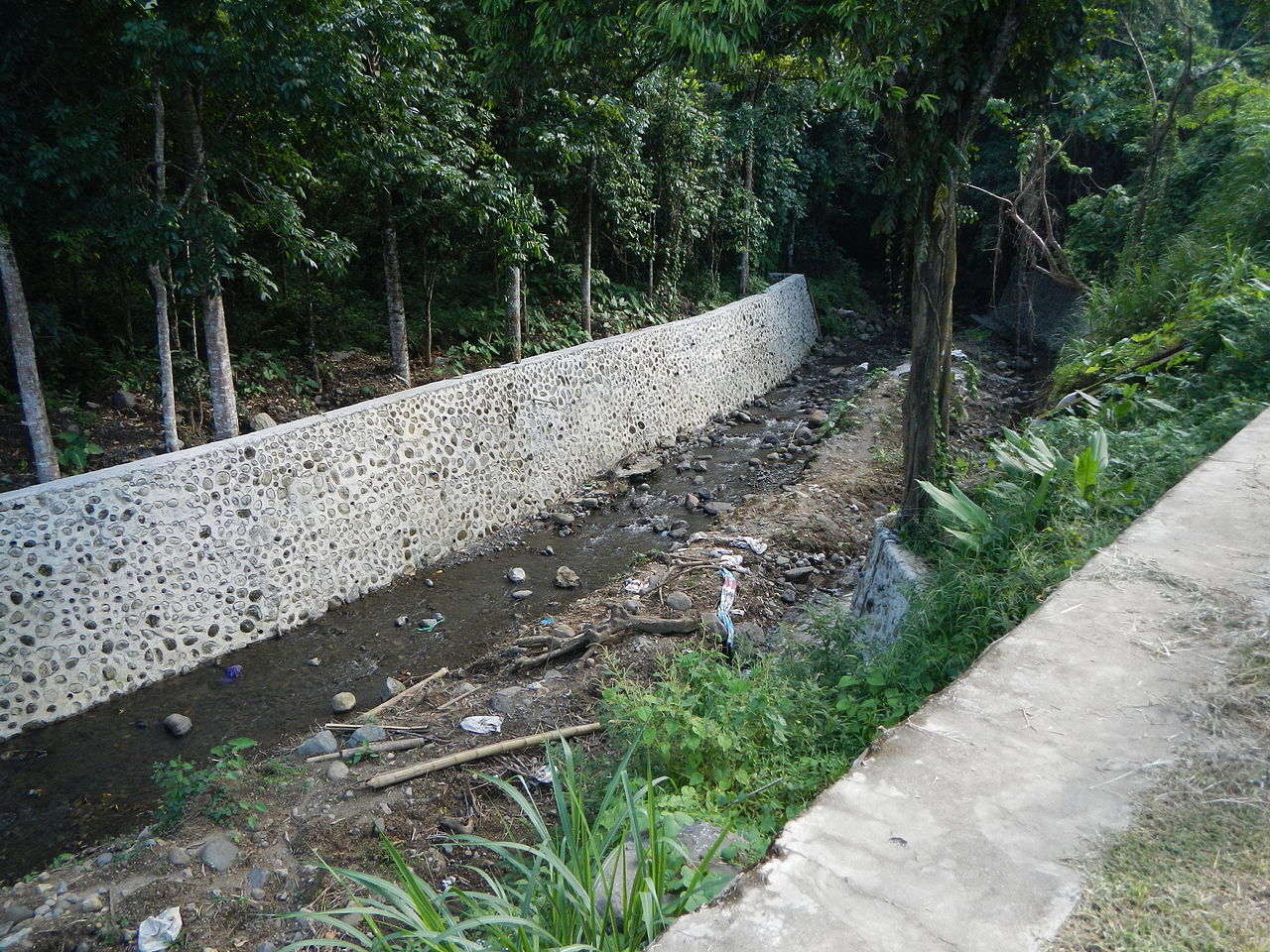

Revetments are sloping structures placed on banks or cliffs in such a way as to absorb the energy of incoming water. River or coastal revetments ar...
Rip rap
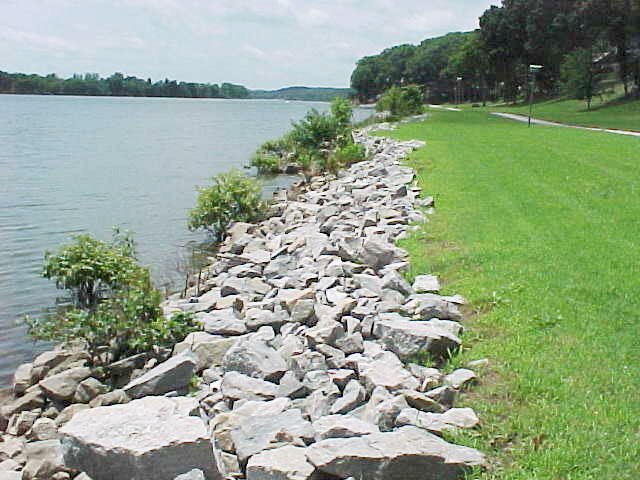

Rip rap is large boulders of rock that are placed along the edge of the coastline and is sometimes referred to as rock armouring. They work by diss...
River Training
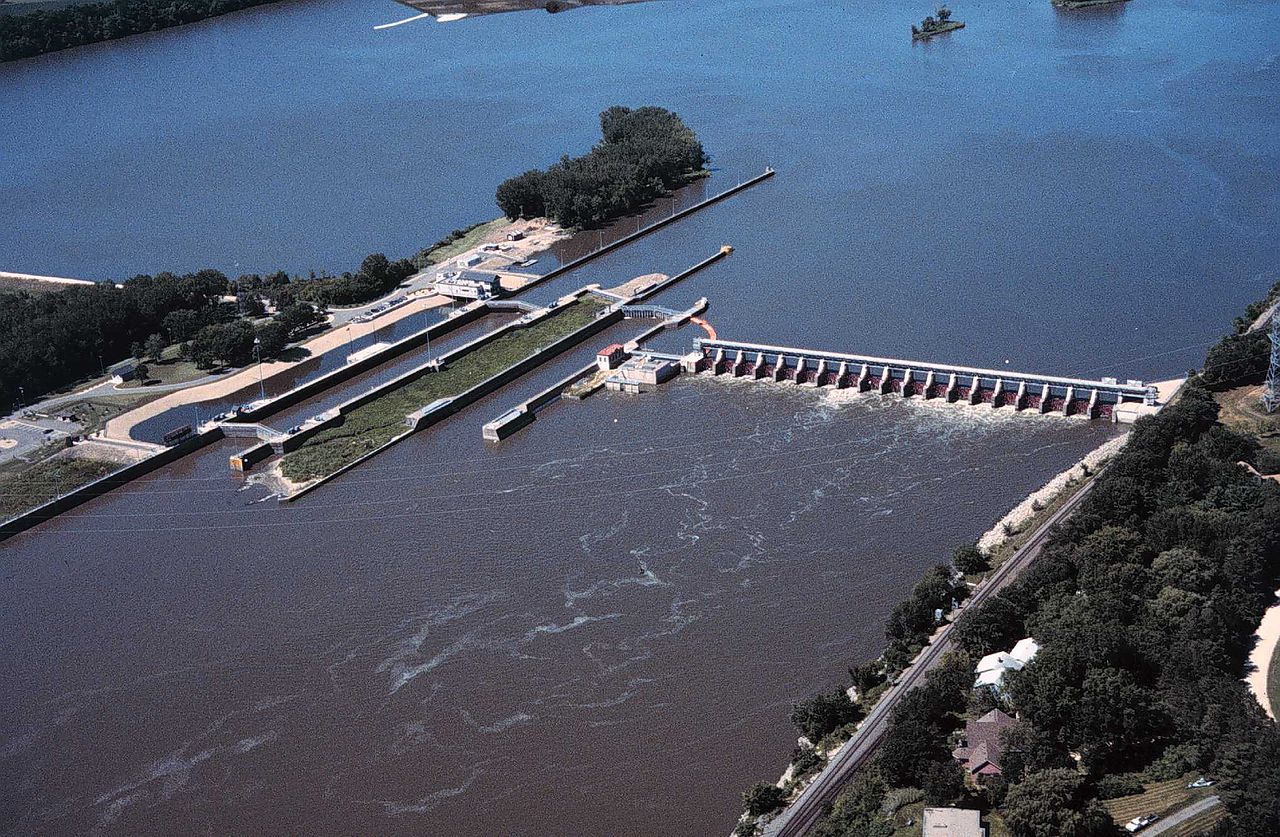

River training refers to the structural measures which are taken to improve a river and its banks. River training is an important component in the ...
Safety margins in new investment
Uncertainties in climate change make it difficult to predict precisely the required degree of protection. Often, when it is cheap, it is sensible t...
Sandbag wall
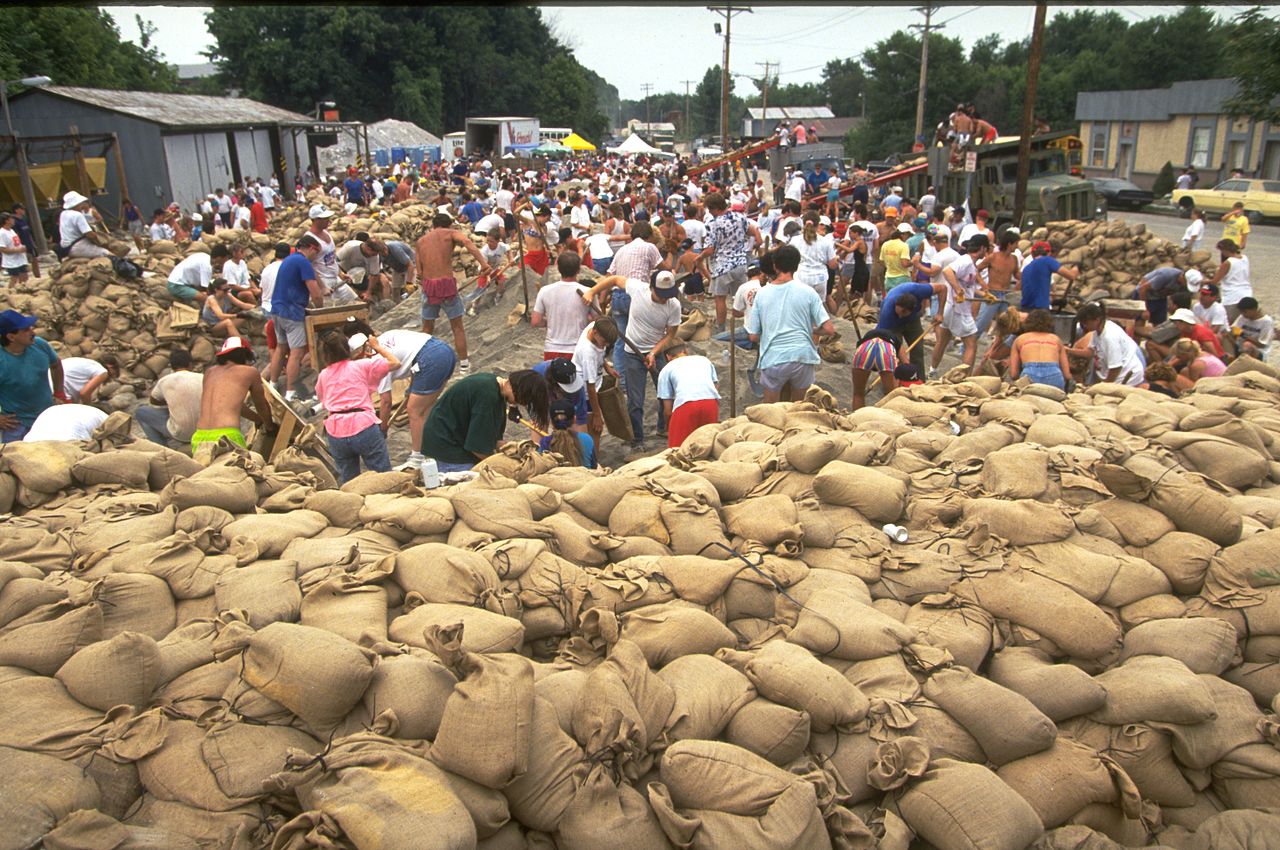

A sandbag is a bag or sack made of hessian / burlap, polypropylene or other materials, that is filled with sand or soil and it is used for flood de...
Seawall
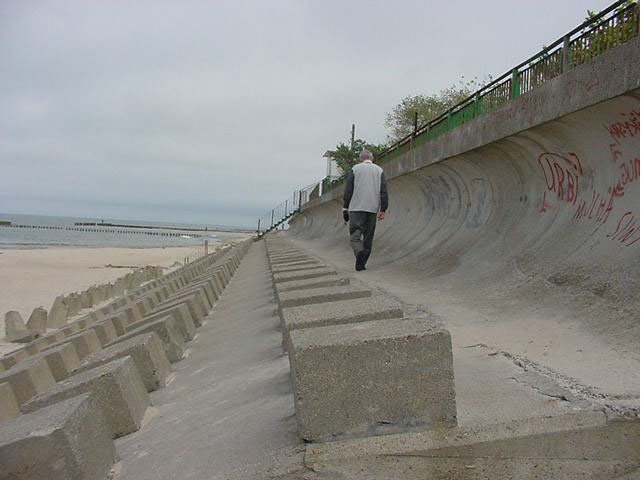

Seawalls are hard engineered structures with a primary function to prevent further erosion of the shoreline. They are built parallel to the shore a...
Sectional barrier
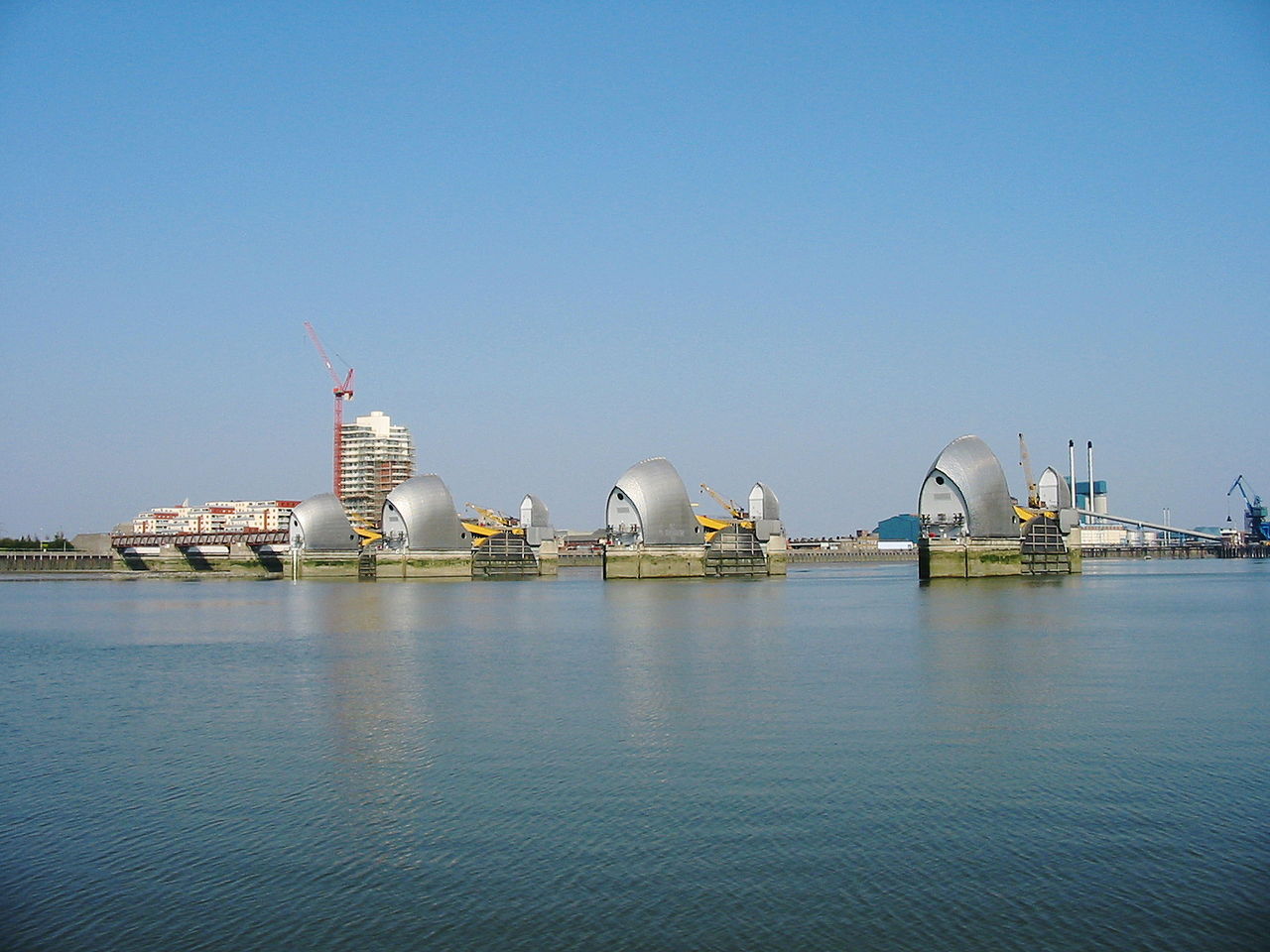

These systems consist of multiple sections made of rigid materials such as steel or fibreglass which are joined or interlocked to form a continuous...
Sediment replenishment
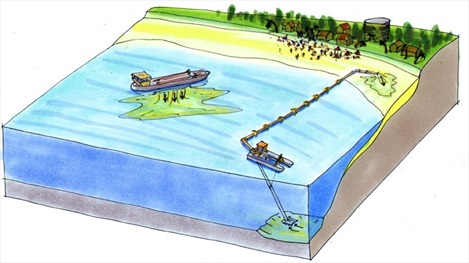
Sediment replenishment method is one of new measures of sediment management mostly used in river systems where dams/reservoirs have been created. I...
Seepage barrier

Seepage barriers are constructed in order to control and mitigate the subsurface flow, or seepage of water. Depending on the method employed, they...
Sludge retention tank in Lake Makria

It is located west of the New Port of Limassol. The existing natural lake was formed and a basin was built at the entrance to hold the mud so it w...
Sluice
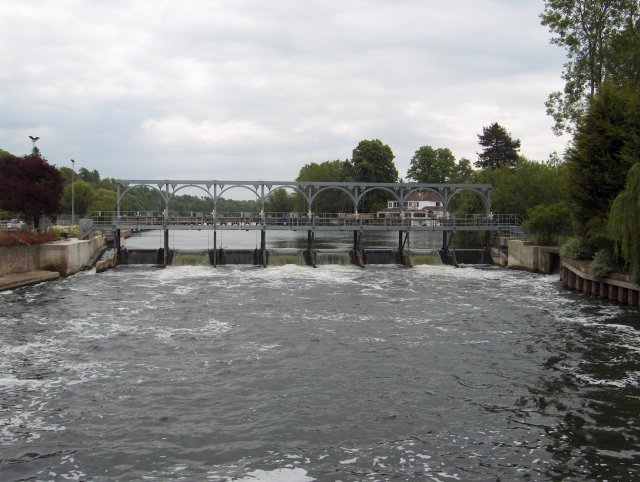

A sluice is a gate used to control the rate of flow of water. It fulfills the function of a flood protection and hinterland drainage. In normal ope...
Soakaway
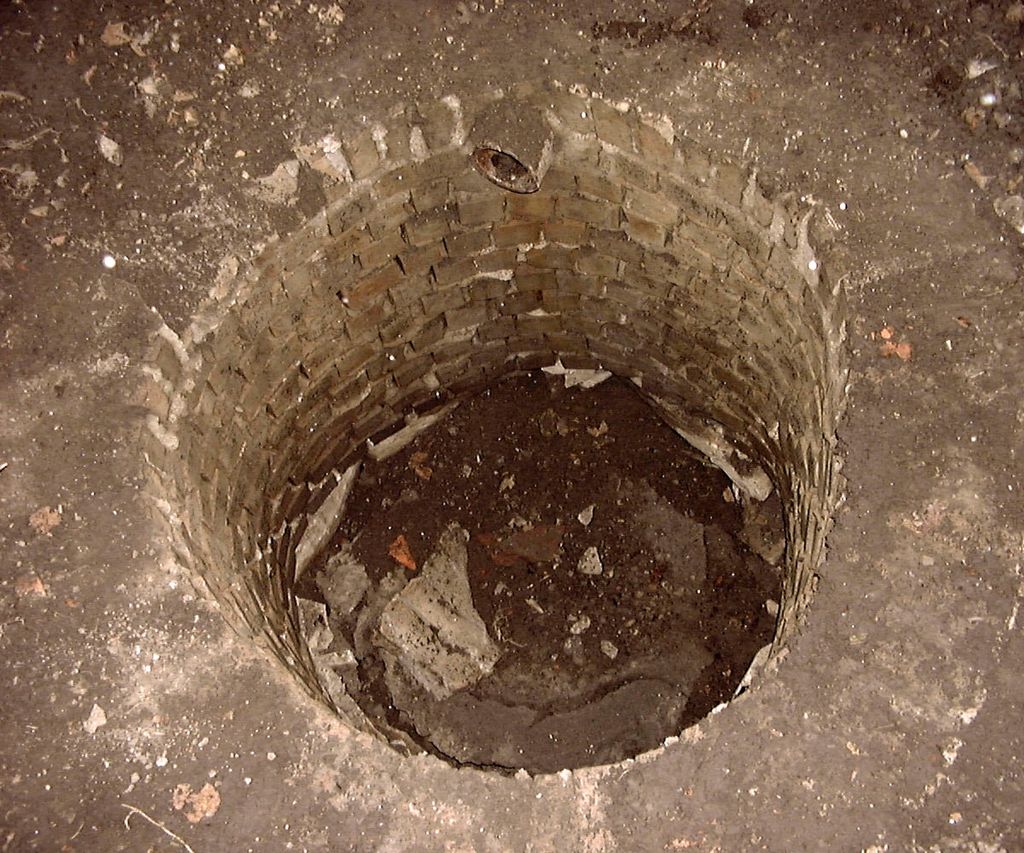

Soakaways are square or circular excavations either filled with rubble or lined with brickwork, pre-cast concrete or polyethylene rings/perforated ...
Social network mapping
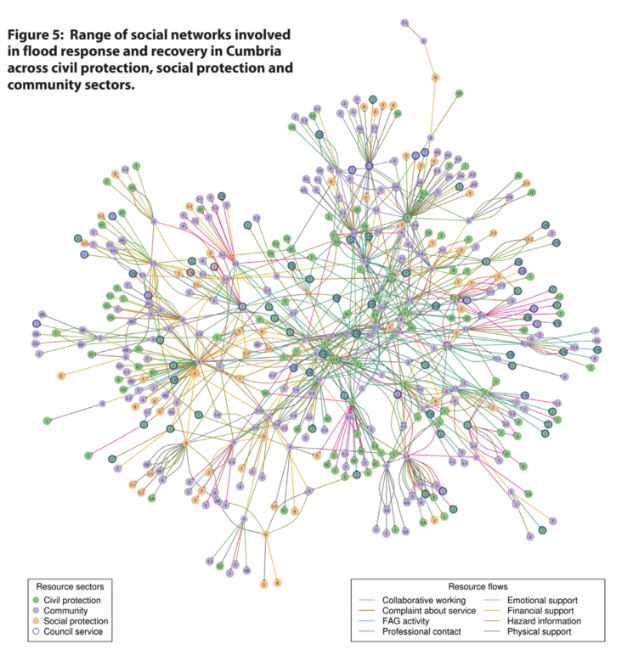
Social network mapping can help stakeholders to locate their place within a wider network, and this network can be communicated and explained to ot...
Stilt house building
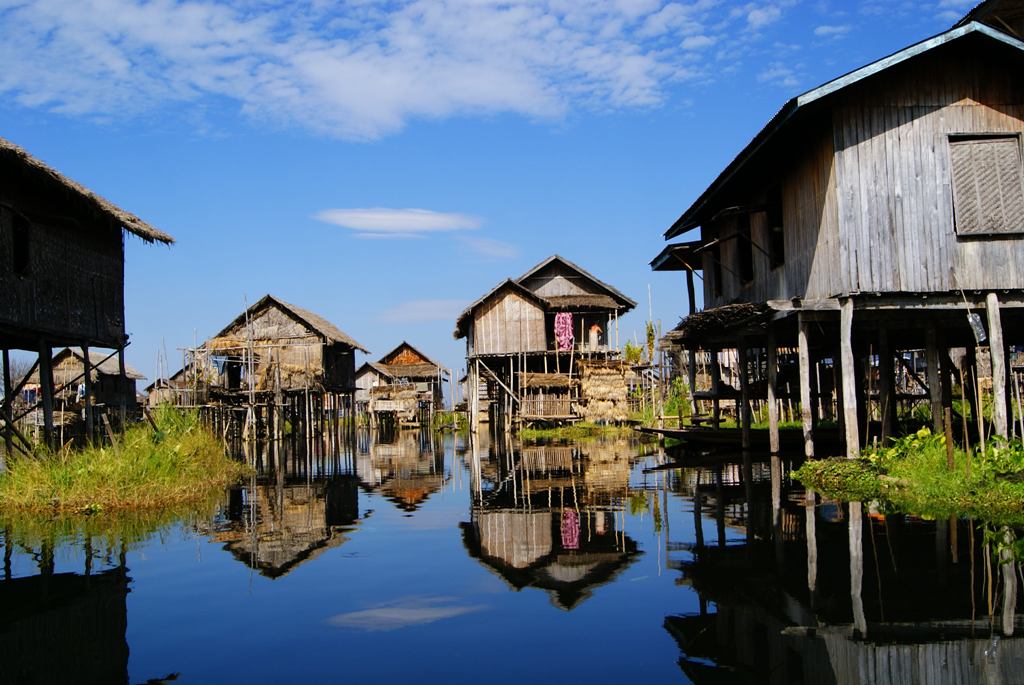

A stilt house is a raised structure that is most commonly built above water, although it also may be built over dirt or sand. It is sometimes calle...
Storm surge barrier
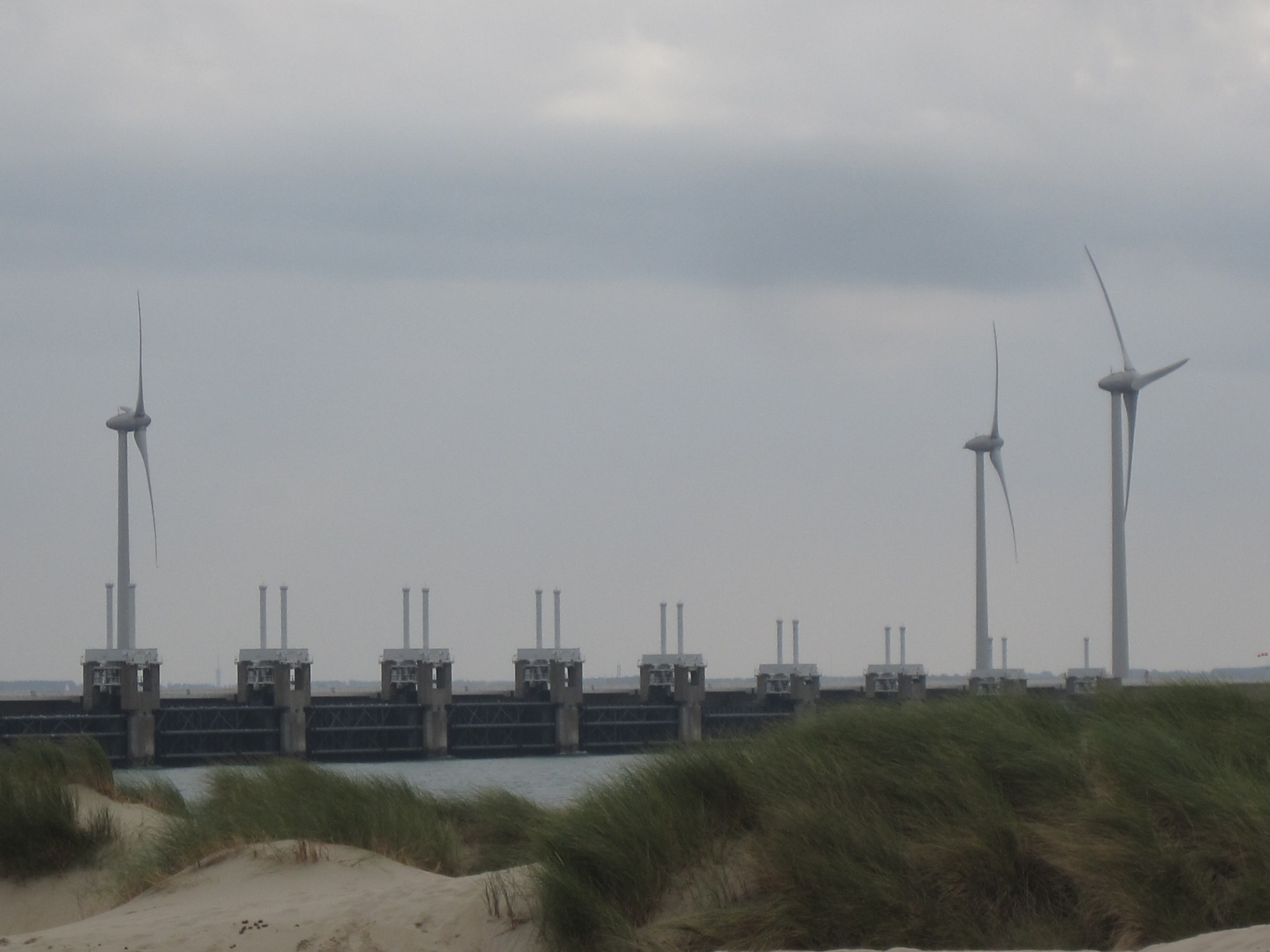

Storm surge barriers are hard engineered structures with a primary function of preventing coastal flooding. Their secondary role is to shorten the ...
Stormwater harvesting system
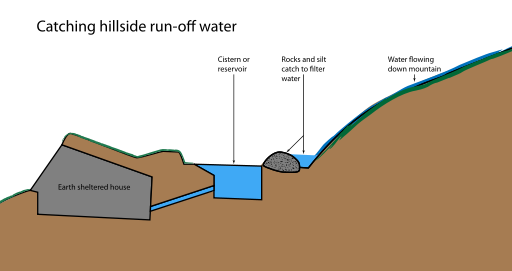
Stormwater harvesting (SWH) consists in collecting, storing and reusing stormwater collected from drains or creeks, on the contrary to rainwater ha...
Stormwater retention tank
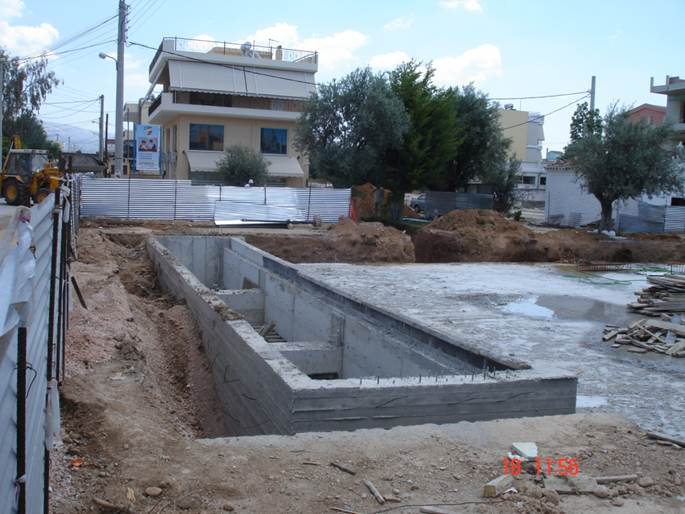

Stormwater tanks are an effective way of reducing peak flow and equalising flow rates from storm water runoffs in the sewer system. Placed strategi...
Sunken lane
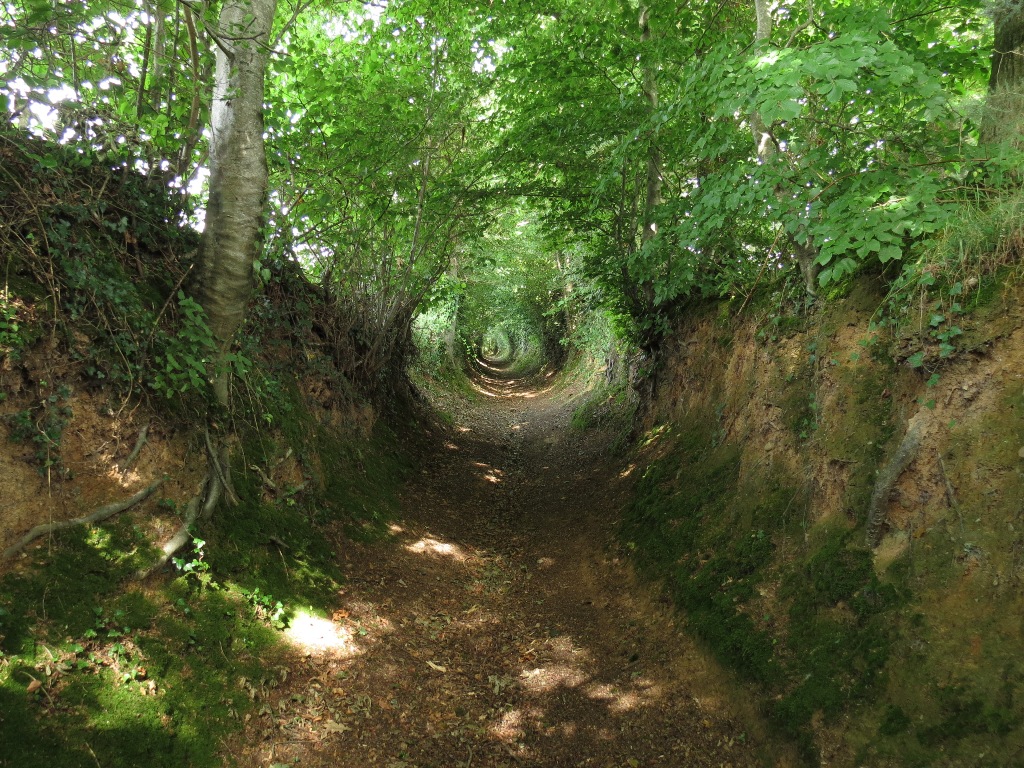

A sunken lane (also hollow way or holloway) is a road or track which is significantly lower than the land on either side, not formed by the (recen...
Swale

A swale is a low tract of land, especially one that is moist or marshy. The term can refer to a natural landscape feature or a human-created one. A...
Tax relief

After a disaster, the government can raise funds for disaster rehabilitation with a tax. Like hedging instruments, a tax spreads the costs of the d...
Toroba
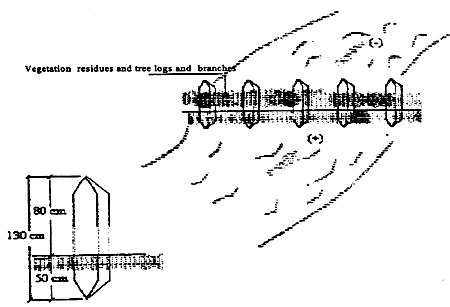
Toroba is a homemade diversion structure that is used to divert flood water for water supply augmentation. It is built of wooden poles, taken from ...
Tubes

Tubes (air filled or water filled) flood protection products are typically pre-fabricated geo-membrane or reinforced PVC tubes filled with air or w...
Unused sewers
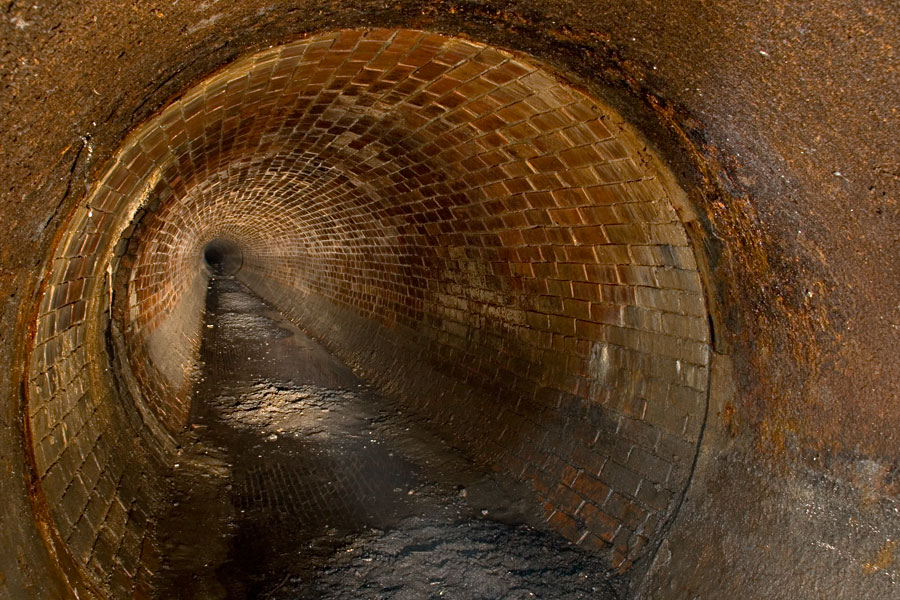

Many towns and cities have large numbers of unused sewers. It is often too expensive to remove them. Giving those unused sewers a second life for r...
Urban forest and park
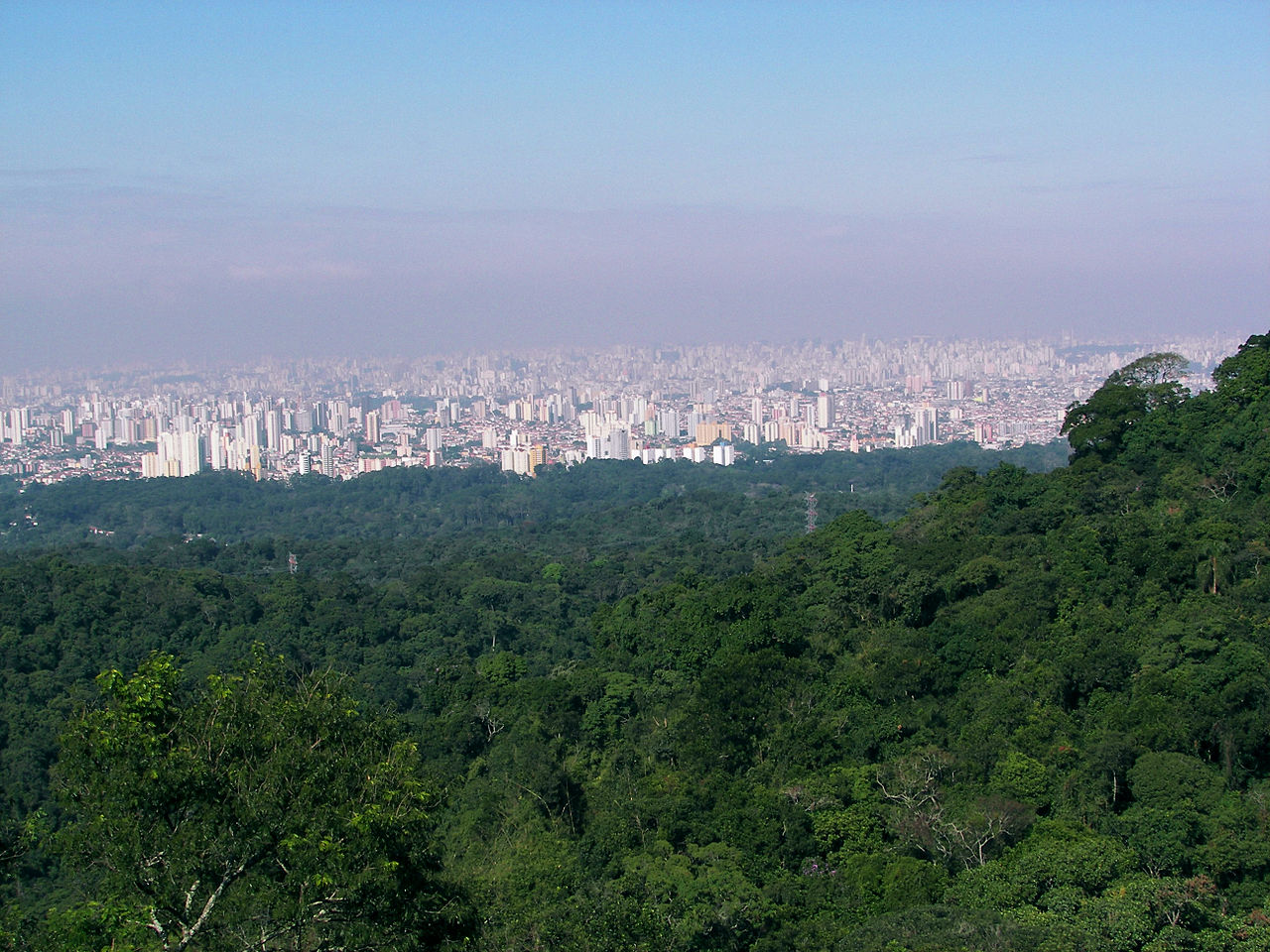

An urban forest is a forest or a collection of trees that grow within a city, town or a suburb. In a wider sense it may include any kind of woody p...
Vulnerability assessment
Vulnerability assessment is important in to consider in risk management and flood damage assessment. Researches with vulnerability subject involves...
Water square
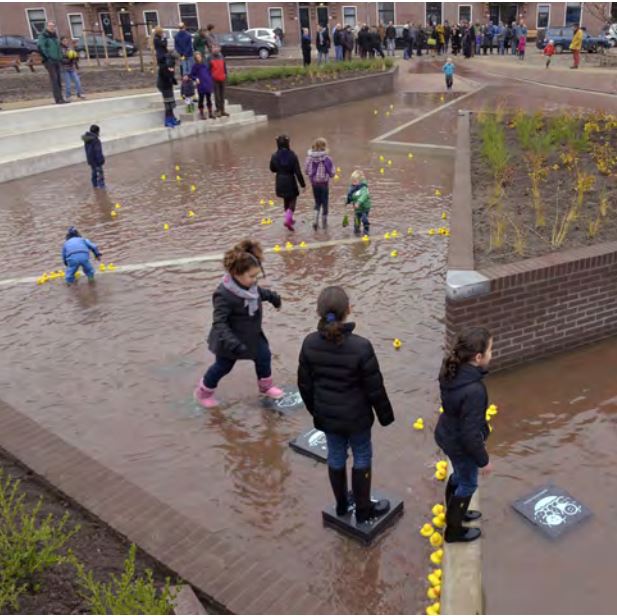

The water square combines water storage with the improvement of the quality of urban public space. It makes money invested in water storage facilit...
Weir
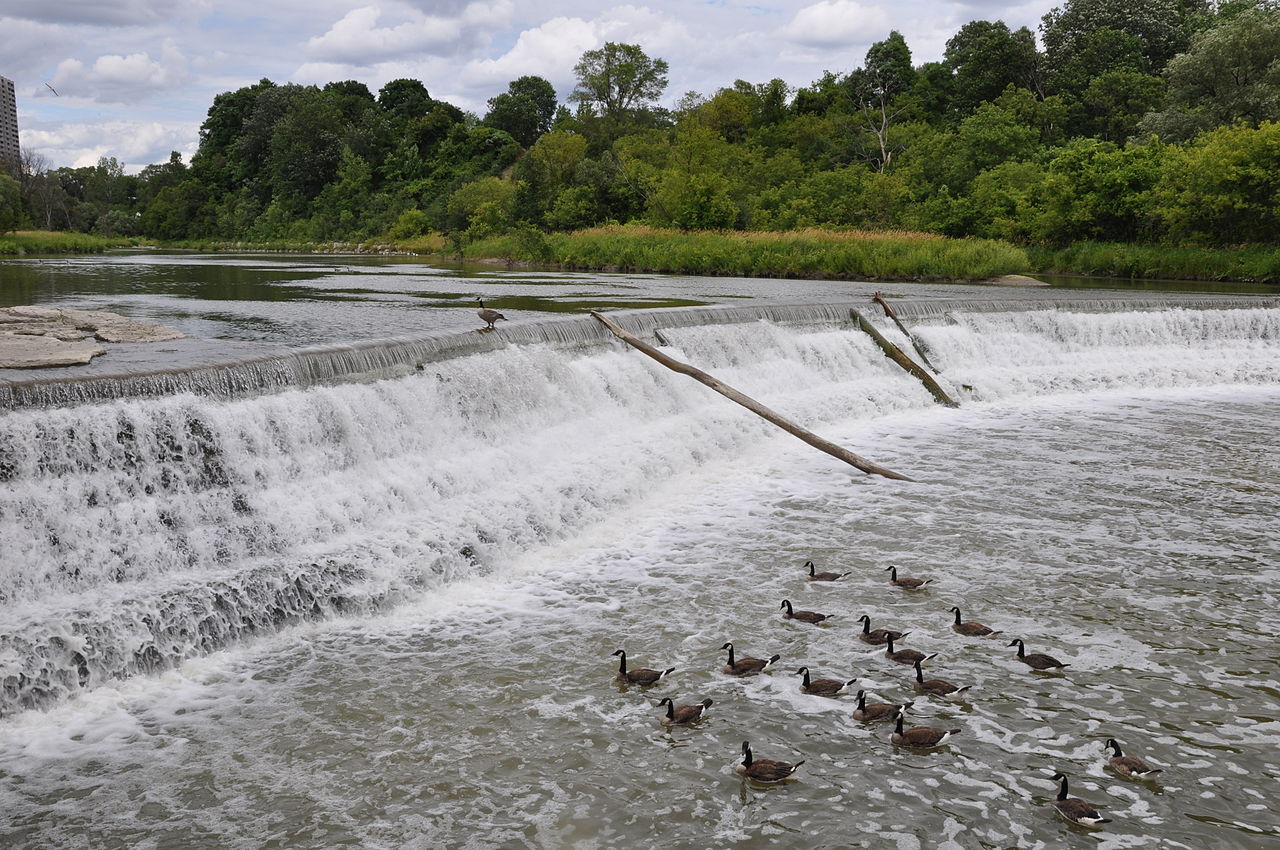

A weir is a barrier across a river designed to alter the flow characteristics. In most cases weirs take the form of obstructions smaller than most ...
Wet-floodproofing technology
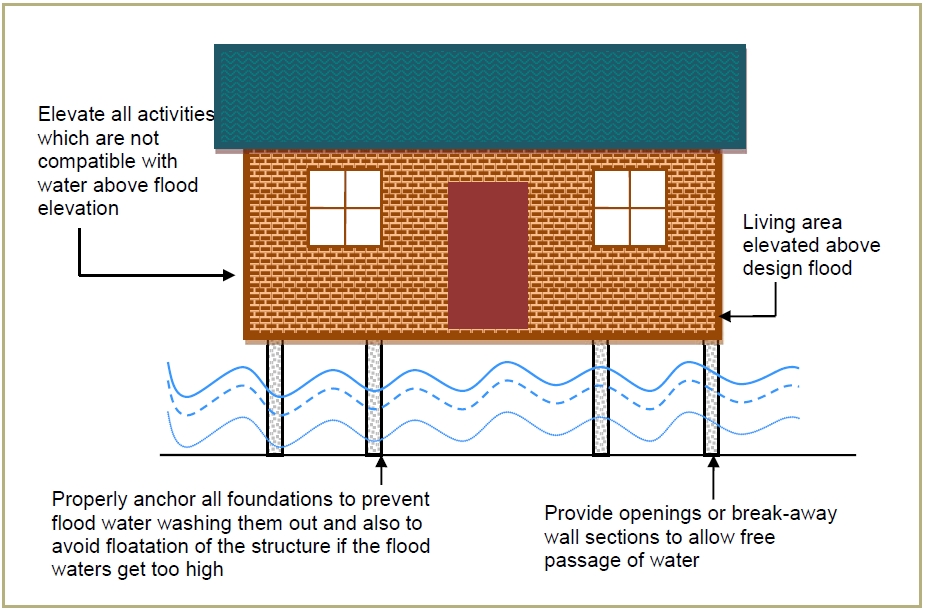
Wet-floodproofing can be an appropriate approach to improve the flood resilience of new and existing buildings, particularly in areas at high flood...
Wetland and wetland restoration
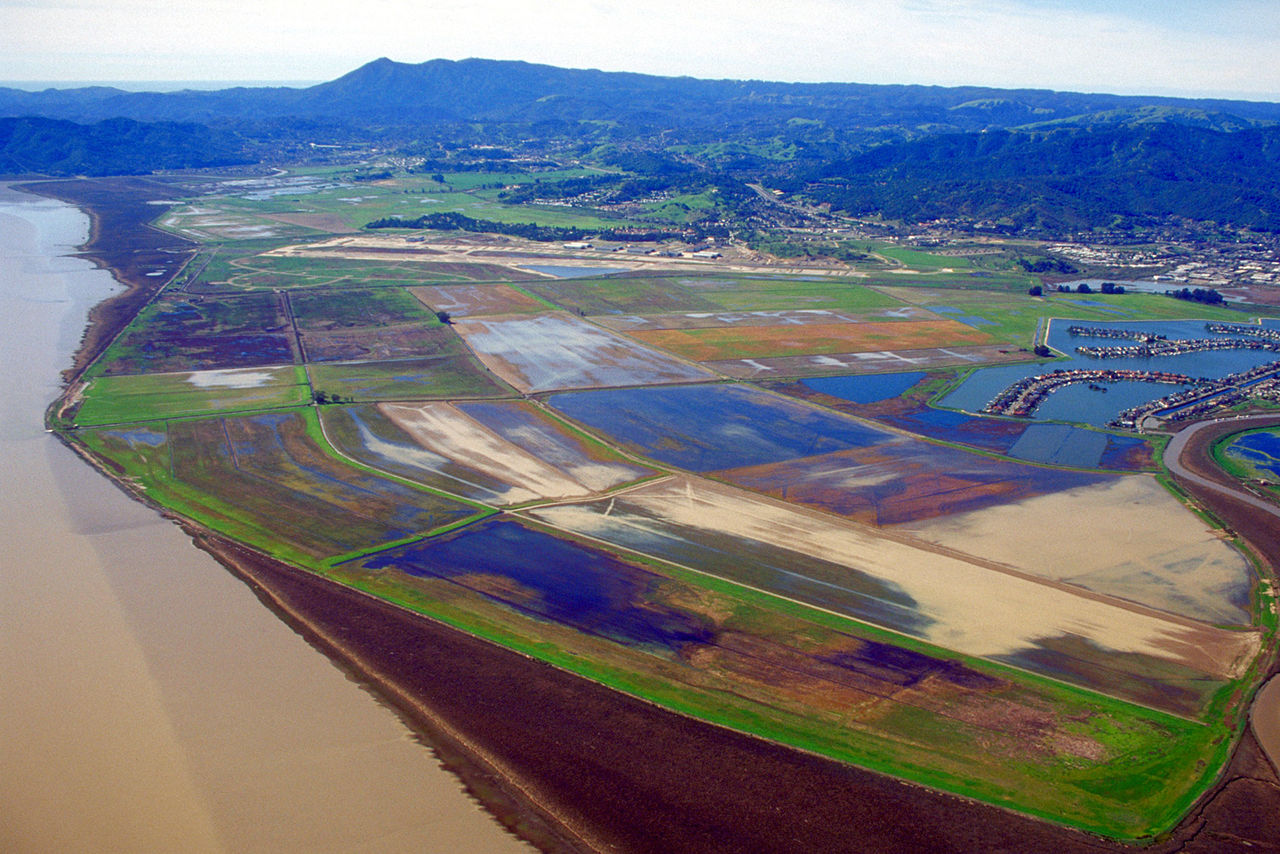

A wetland (Natural or Constructed/Artificial) is a land area that is saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally, such that it takes on ...
Wharf
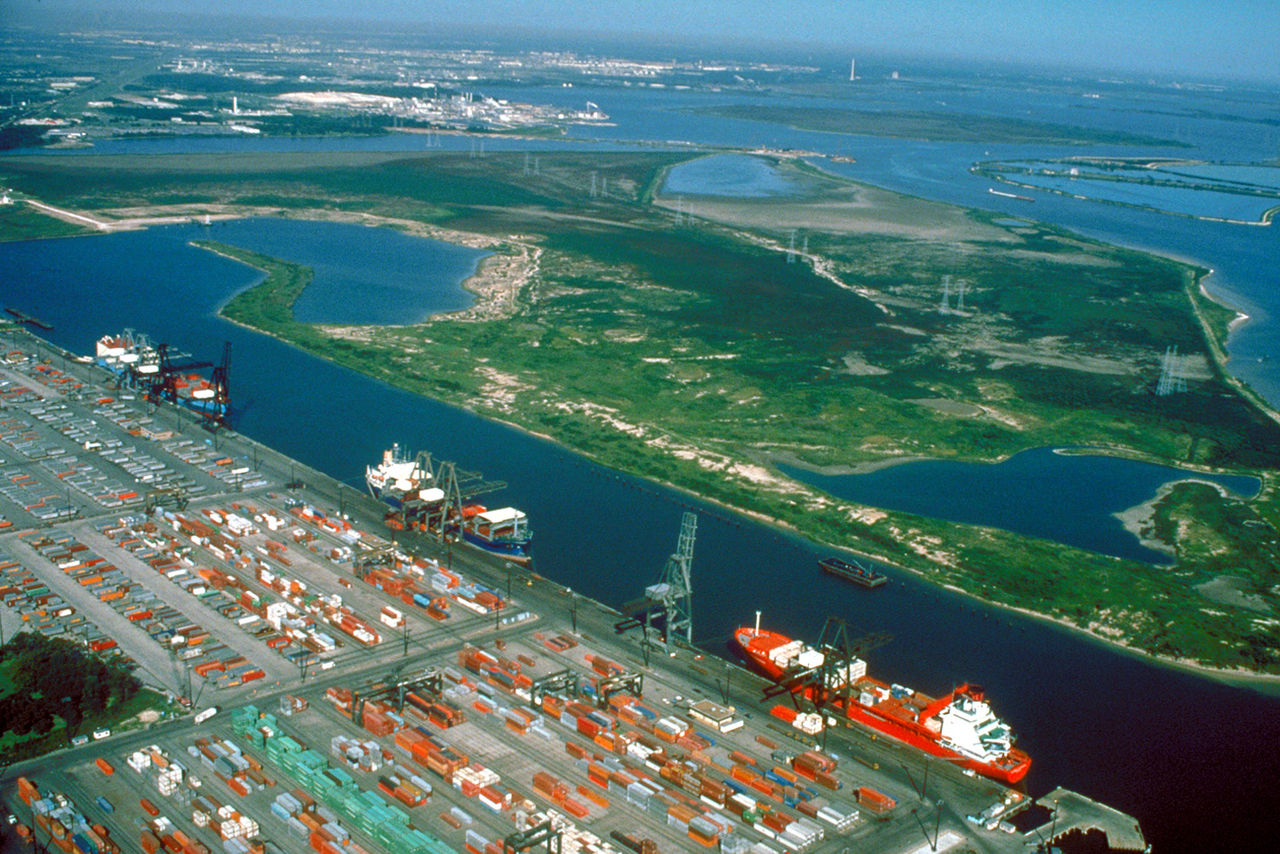

Wharf is the oldest term in English referring to port structures. It denotes any structure of timber, masonry, cement, or other material built alon...

Flood management measures
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Adjustment of waterway | Adjustment of the waterway contains every constructional measure to a navigable channel, e.g. Broadening of curved waterways, deepening of the ... |
| Afforestation | Land use conversion is a general term for large scale geographic change. Afforestation is one such land conversion in which ... |
| Amphibious building | Amphibious buildings lie on the ground out of flood periods and are likely to float when the water level rises ... |
| Aquifer recharge | Aquifer recharge is achieved by adding surface water in basins, furrows, ditches, wells or other facilities where it infiltrates into ... |
| Artificial sand dunes and dune rehabilitation | Naturally occurring sand dunes are wind-formed sand deposits representing a store of sediment in the zone just landward of normal ... |
| Beach nourishment | Beach nourishment is an adaptation technology primarily used in response to shoreline erosion, although flood reduction benefits may also occur. ... |
| Bioretention area | A bioretention area is a stormwater treatment system that is a depression integrated into the landscape. A bioretention area captures ... |
| Breakwater | Breakwaters are structures constructed on coasts as part of coastal defense or to protect a port and port entrance from ... |
| Budget diversion | Governments of emerging-economy countries raise money for disaster response and rehabilitation by diverting funds from other budgeted items such as ... |
| Building elevation | Building elevation is a measure mainly suitable for new constructions, but it can also be applied on existing buildings. The ... |
| Building relocation | A building relocation is the process of moving a building from one location to another. There are two main methods ... |
| Buildings as flood defence | New and existing buildings in flood risk areas can be used as flood defence. The buildings should be completely integrated ... |
| Building without a crawlspace | Crawlspaces vent the underside of a building and thereby prevent the moulding of dry wooden floors. However, with the introduction ... |
| Bypass channel | Bypass channel, also known as a flood-relief channel, is an artificially made waterway constructed in order to protect urban and ... |
| Canal and rill | Canals and rills are open surface water channels with hard edges. They are simply channels that water flows along whereby ... |
| Cascading flood compartment system | The “system of cascading flood compartments” combines area prevention with constructional solutions. The idea is to (re)build a second dikeline ... |
| Check valve | A check valve or non-return valve is installed in pipes which are vulnerable for backflow in flood conditions. Backflow is ... |
| Coastal setback | Coastal setbacks are a prescribed distance to a coastal feature such as the line of permanent vegetation, within which all ... |
| Community involvement | Community involvement is a bottom up approach which involves the community in decision-making process. For example, communities living in flood-prone ... |
| Conventional urban drainage systems | The purpose of urban drainage systems (a.k.a. collection systems) is to enable safe and reliable disposal of stormwater runoff (i.e., ... |
| Creation of a second dike line | A second dike line is created by building other dikes, mostly bigger dikes, on the water side of existing dikes, ... |
| Data collection | Data collection is the process of gathering and measuring information on targeted variables in an established systematic fashion, which then ... |
| Deculverting of watercourses | This activity involves techniques to resolve the issues created by culverted watercourses. This is predominantly through deculverting, or ‘daylighting’ which ... |
| Demountable flood protection barrier | Demountable flood protection barriers consist of a combination of removable and pre-installed permanent components. The system is planned to be ... |
| Dike | A dike or levee is an elongated artificially constructed embankment, which protects low-lying areas against higher water levels. It is ... |
| Dike inspection and/or recovery | Inspection of the flood protection dikes takes place in order to observe and assess the state of the dike and ... |
| Dike reinforcement | Dike reinforcement describes the process of strengthening the dike by e.g. raising the dike height, widening of the dike crest, ... |
| Dike relocation | A new dike is built further away from the river or the coast after which the existing dike is removed. ... |
| Ditch | A ditch is usually defined as a small to moderate depression created to channel water. A ditch can be used ... |
| Dredging of watercourse | The term dredging is used to refer to the systematic removal of accumulated material from river or other watercourse channels. ... |
| Dry-floodproofing technology | Dry floodproofing is a method of flood preparation that involves building designs and material choices that do not allow for ... |
| Dwelling mound | A dwelling mound is an artificial hill made from earth, created to provide safe ground for humans and animals during ... |
| Elaboration of municipal archives on major hazards | Through municipal archives, citizens will be able to be kept informed about both the natural and technological risks to which ... |
| Emergency exit of buildings above highest flood level | The main exit of a building is traditionally positioned at ground level. In case of a flood this only exit ... |
| Emergency operation centre and personnel | An Emergency Operation Centre (EOC) is a central location where response personnel can coordinate and make decisions in support of ... |
| Emergency supplies and utilities | Emergency supplies and utilities are necessary in case of a flood emergency. It should consist of food and drinks, first ... |
| EU Flood Risk Management Directive | EU adopted the Flood Risk Management Directive. Directive 2007/60/EC on the assessment and management of flood risks entered into force ... |
| Evacuation plan | The purpose of evacuation is to relocate people temporarily from areas at risk of the consequences of flooding to places ... |
| Evacuation routes at elevated level | Evacuation routes at an elevated level are necessary as a route for safe evacuation in flood events. They should be ... |
| Family emergency planning | Disasters and emergencies such as floods can affect people in any part of the world and at any time of ... |
| Fascine | A fascine is a bundle of sticks or brushwood used in construction, generally to strengthen an earthen structure, fill ditches, ... |
| Filled container | These are cellular barriers filled with aggregates or water to form a barrier against floodwater. Containers can be divided into ... |
| Filter drain | A filter drain is a gravel filled trench, generally with a perforated pipe at the base. Runoff flows slowly through ... |
| Filter strip | Filter strips are gently sloping, vegetated strips of land that provide opportunities for slow conveyance and infiltration (where appropriate). They ... |
| Filter trench | Filter trenches are shallow excavations filled with rubble or stone that create temporary subsurface storage of stormwater runoff. These trenches ... |
| Flexible water level management | Flexible water level management involves anticipating precipitation that has been forecast. The water level is lowered before a shower is ... |
| Floating agricultural system | Floating agriculture is a way of utilising areas which are waterlogged for long periods of time in the production of ... |
| Floating building | The basic characteristic of floating buildings is that they are not supported by a firm foundation, but float on water. ... |
| Floating road | Road transport infrastructure and evacuation routes that are prone to flooding need to be flood proofed to reduce the vulnerability ... |
| Flood control dam | A flood control dam is a dam built to catch surface runoff and stream water flow in order to regulate ... |
| Flood detention reservoir | Flood detention reservoir, also known as an attenuation or balancing or flood control reservoir or detention basin, collects water at ... |
| Flood emergency framework | Flood emergency framework sets out the government’s strategic approach to achieving the aims set out below and is intended for ... |
| Flood forecasting and early warning | Flood forecasting is an important component of flood warning. Flood forecasting involves prediction of water levels and flows at particular ... |
| Flood gate | These barriers are made of a single or pair of rigid sections (usually steel or fibreglass), designed to close a ... |
| Flood hazard mapping | Flood hazard mapping is an exercise to define those areas which are at risk of flooding under extreme conditions. As ... |
| Flood insurance | Flood insurance is an important risk management tool that can be applied at various levels: individual, corporate and government. It ... |
| Floodplain excavation | Floodplain excavation is a measure by which gradual height increase caused by sedimentation on flood plains may be counteracted. The ... |
| Flood proof infrastructure | Evacuation routes and infrastructure in cities that are prone to flooding need to be flood proofed. Available options to reduce ... |
| Flood shelter | Flood shelters are created in areas which experience severe flooding. Elevated flood shelters should be constructed above the highest expected ... |
| Floodwall | A floodwall is a primarily vertical artificial barrier designed to temporarily contain the water of a river or other waterway ... |
| Frame barrier | Frame barriers consist of rigid frames with impermeable membranes or sections spanning between them. They rely on supporting frames and ... |
| Freestanding barrier | These modular systems are made of impermeable materials and are joined together to form a continuous barrier or wall. These ... |
| Government debt instrument | A common way for emerging-economy governments to raise funds after a disaster is to borrow from their central bank reserves ... |
| Grated channels | Grated channels collects water at the side of the road and can channel water in storm drains into the harbour. |
| Green roof | Green roof belongs in the category of SUstainable Drainage Systems (SUDS) and aims at source controlling. A green roof or ... |
| Green wall | A green wall is a wall partially or completely covered with vegetation that includes a growing medium, such as soil. ... |
| Groyne | A groyne is normally a straight structure perpendicular to the shoreline. Groynes work by blocking (part of) the littoral drift, ... |
| Gutter | A gutter is a non-permeable open drain to collect transport rainwater. Usually a gutter runs along a road. It is ... |
| High water mark | A high water flood mark is a point that represents the maximum rise of a body of water over land. ... |
| Hydraulic filling | Hydraulic Fill is fill in which the materials are deposited by a flowing stream of water. This fill material will ... |
| Hydrological and Meteorological Observatory | Hydrological and Meteorological Observatory is an observation service dedicated to long-term monitoring of climatological and hydrological changes. It gathers data ... |
| Improved construction site preparation | Improved construction site preparation is focused on improving the strength and drainage capabilities of an area that is converted from ... |
| Increased capacity of sewer/drainage system | Increasing the capacity of the sewer/drainage system increases the ability of the system to drain excess surface water during heavy ... |
| Increase of infiltration capacity | Improving the soil infiltration capacity means improving the permeability of the soil. If the infiltration capacity of the soil is ... |
| Independent commission for flood and disaster risk reduction | An Independent commission is a politically independent executive arm. It is alone responsible for drawing up proposals for new legislation. ... |
| International loan | Emerging-economy governments have the opportunity to borrow at low interest rates from international lending organizations aiming at pre-disaster planning or ... |
| Land claim | The main objective of land claim is neither erosion nor storm reduction. The aim of land claim is instead, to ... |
| Land use plan / spatial planning | Spatial planning systems are the methods used by the public sector to influence the distribution of people and activities in ... |
| Limassol Drainage Master Plan | Storm-Water, Drainage Master Plan was prepared by SBLA in 1992. In 2003 it was updated. About 60% has been implemented. |
| Living with water - principles | The pursuit of a safe, healthy and sustainable water management is of national interest in the Netherlands. Themes like "water ... |
| Maintenance of hydraulic structures of the storm drainage system | Set up regulations on maintenance of the hydraulic structures and drainage network infrastructures so that their maximum conveyance capacity will ... |
| Managed realignment | Managed realignment or managed retreat allows an area that was not previously exposed to flooding by the sea to become ... |
| Monitoring and flood forecasting through partnerships | Organizing and recording partnerships between the various actors so that optimal responsiveness of the population can be produced in case ... |
| Multi-functional flood defences | Multifunctional Flood Defences (MFD) is a newly developed concept to optimize allocation of urban space rather than constructing stand-alone structures. ... |
| Multi-layer safety as a central concept for flood protection | The central concept for the revised water safety policy is formed by 'multi-layer safety'. In this concept safety is assured ... |
| Multi-level capacity building | According to the UNDP, in the global context, capacity refers to the ability of individuals and institutions to make and ... |
| Municipal flood control plan | The municipal plan expresses the shared goals, objectives and priorities of a community and allows its members to work together ... |
| Network of waterways | Ένα δίκτυο εσωτερικής ναυσιπλοΐας εστιάζει κυρίως στη διασύνδεση των υδάτινων σωμάτων που βρίσκονται σε κοντινές αποστάσεις. Συνδέοντάς τα, με υπόγεια ... |
| Permeable paving | Permeable paving is a range of sustainable materials and techniques for permeable pavements with a base and sub base that ... |
| Polder | A polder is a low-lying tract of land enclosed by embankments (barriers) known as dikes that forms an artificial hydrological ... |
| Pond | A pond is a body of standing water, either natural or artificial, that is usually smaller than a lake. They ... |
| Port restructuring | Restructuring of the layout of the port, its equipment and flood protection system. |
| Prescription on the construction code | Impose implementation of measures for mitigation and vulnerability reduction through the construction code of town planning. (ASFPM, Modifications to Existing ... |
| Public awareness, information, education and communication | Inform local citizens and visitors about the major hazards through public meetings, flyers, website, training, collaborative platforms, brochures, public presentations, ... |
| Pumping station | A pumping station is used to discharge water out of an area. It can be used to transport sewer water ... |
| Rain garden | A rain garden is a planted depression or a hole that allows rainwater runoff from impervious urban areas, like roofs, ... |
| Rainwater disconnection | Rainwater disconnection, i.e. the separation of the sewage system from the rainwater discharge system, is also a solution to prevent ... |
| Rainwater harvesting system | The term rainwater harvesting refers to reuse of stored water, including water purification, and can form part of a sustainable ... |
| Rainwater storage beneath sports fields | One option for creating additional water storage facilities is storing in underground crates. This is a hidden technology that fits ... |
| Raised kerb | Kerb or curb is the edge of the pavement at the side of the road. Water can be channeled along ... |
| Red alert exercise | A red alert emergency exercise enables the simulation/testing of population/authorities response and plans in case of an extreme flood event ... |
| Rescue plan | The aim of flood rescue operations is to move people from immediate or potential harm to safety. Failed evacuation operations ... |
| Reserve funds | Building a catastrophic reserve fund is one of the measures assisting risk management as it will enable claims to be ... |
| Retention of rainwater in the vicinity of a roundabout | In case of an extreme event the surface runoff is conveyed by the streets to a roundabout, where it is ... |
| Revetment | Revetments are sloping structures placed on banks or cliffs in such a way as to absorb the energy of incoming ... |
| Rip rap | Rip rap is large boulders of rock that are placed along the edge of the coastline and is sometimes referred ... |
| River Training | River training refers to the structural measures which are taken to improve a river and its banks. River training is ... |
| Safety margins in new investment | Uncertainties in climate change make it difficult to predict precisely the required degree of protection. Often, when it is cheap, ... |
| Sandbag wall | A sandbag is a bag or sack made of hessian / burlap, polypropylene or other materials, that is filled with ... |
| Seawall | Seawalls are hard engineered structures with a primary function to prevent further erosion of the shoreline. They are built parallel ... |
| Sectional barrier | These systems consist of multiple sections made of rigid materials such as steel or fibreglass which are joined or interlocked ... |
| Sediment replenishment | Sediment replenishment method is one of new measures of sediment management mostly used in river systems where dams/reservoirs have been ... |
| Seepage barrier | Seepage barriers are constructed in order to control and mitigate the subsurface flow, or seepage of water. Depending on the ... |
| Sludge retention tank in Lake Makria | It is located west of the New Port of Limassol. The existing natural lake was formed and a basin was ... |
| Sluice | A sluice is a gate used to control the rate of flow of water. It fulfills the function of a ... |
| Soakaway | Soakaways are square or circular excavations either filled with rubble or lined with brickwork, pre-cast concrete or polyethylene rings/perforated storage ... |
| Social network mapping | Social network mapping can help stakeholders to locate their place within a wider network, and this network can be communicated ... |
| Stilt house building | A stilt house is a raised structure that is most commonly built above water, although it also may be built ... |
| Storm surge barrier | Storm surge barriers are hard engineered structures with a primary function of preventing coastal flooding. Their secondary role is to ... |
| Stormwater harvesting system | Stormwater harvesting (SWH) consists in collecting, storing and reusing stormwater collected from drains or creeks, on the contrary to rainwater ... |
| Stormwater retention tank | Stormwater tanks are an effective way of reducing peak flow and equalising flow rates from storm water runoffs in the ... |
| Sunken lane | A sunken lane (also hollow way or holloway) is a road or track which is significantly lower than the land ... |
| Swale | A swale is a low tract of land, especially one that is moist or marshy. The term can refer to ... |
| Tax relief | After a disaster, the government can raise funds for disaster rehabilitation with a tax. Like hedging instruments, a tax spreads ... |
| Toroba | Toroba is a homemade diversion structure that is used to divert flood water for water supply augmentation. It is built ... |
| Tubes | Tubes (air filled or water filled) flood protection products are typically pre-fabricated geo-membrane or reinforced PVC tubes filled with air ... |
| Unused sewers | Many towns and cities have large numbers of unused sewers. It is often too expensive to remove them. Giving those ... |
| Urban forest and park | An urban forest is a forest or a collection of trees that grow within a city, town or a suburb. ... |
| Vulnerability assessment | Vulnerability assessment is important in to consider in risk management and flood damage assessment. Researches with vulnerability subject involves diverse ... |
| Water square | The water square combines water storage with the improvement of the quality of urban public space. It makes money invested ... |
| Weir | A weir is a barrier across a river designed to alter the flow characteristics. In most cases weirs take the ... |
| Wet-floodproofing technology | Wet-floodproofing can be an appropriate approach to improve the flood resilience of new and existing buildings, particularly in areas at ... |
| Wetland and wetland restoration | A wetland (Natural or Constructed/Artificial) is a land area that is saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally, such that ... |
| Wharf | Wharf is the oldest term in English referring to port structures. It denotes any structure of timber, masonry, cement, or ... |


 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά