Definition
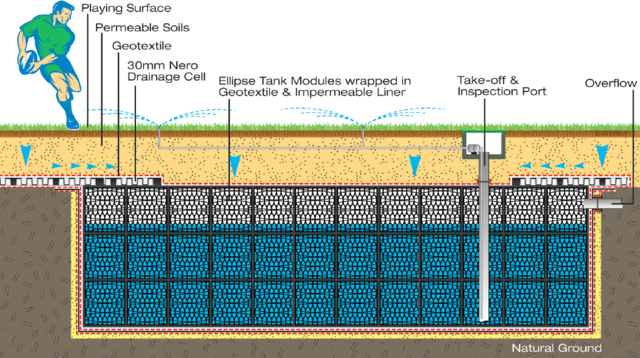
One option for creating additional water storage facilities is storing in underground crates. This is a hidden technology that fits the criteria of sustainable urban planning. An interesting form of multiple uses of single spaces is realising water storage beneath sports fields. The technical aspects are simple to achieve using storage boxes/bulbs. Sports fields can be integrated into water systems in one of two ways. Firstly, the water storage facility is connected directly to surface water. In this scenario, the water level below the sports fields rises according to the surface water level. This is a simple system to operationalise. Fluctuations in the water levels are limited by the maximum fluctuation of the surface water level. Secondly, the water storage facility is not connected directly to surface water. In this scenario, the water that needs storing is fed in from elsewhere, stored and drained at a delayed pace. This allows for more water to be stored, since greater fluctuations in water levels are possible. (Urban Green-Blue Grids for sustainable and resilient cities, Rainwater storage beneath sports fields, accessed on Sept. 2016)Co-benefits and impacts
Apart from reducing runoff during precipitation and flood events, rainwater storage beneath sports fields enables the multifunctional use of the specific area without causing any aesthetic damage of the landscape.Definition (GR)
Μία επιλογή για τη δημιουργία πρόσθετων εγκαταστάσεων αποθήκευσης όμβριων υδάτων, είναι η αποθήκευση σε υπόγειους κλωβούς. Πρόκειται για μια κρυφή εγκατάσταση, που ανταποκρίνεται στα κριτήρια του βιώσιμου αστικού σχεδιασμού. Μια ενδιαφέρουσα μορφή πολλαπλών χρήσεων σε συγκεκριμένους χώρους, αποτελεί η αποθήκευση όμβριων υδάτων κάτω από αθλητικές εγκαταστάσεις. Οι τεχνικές υποδομές είναι απλές στην υλοποίηση, με τη χρήση κουτιών/βολβών αποθήκευσης. Οι αθλητικές εγκαταστάσεις μπορούν να ενσωματωθούν στα συστήματα ύδρευσης με έναν από τους εξής δύο τρόπους. Ο πρώτος τρόπος αφορά την απευθείας σύνδεση της εγκατάστασης αποθήκευσης υδάτων με τα επιφανειακά ύδατα. Σε αυτό το σενάριο, η στάθμη του νερού κάτω από τις αθλητικές εγκαταστάσεις αυξάνεται ανάλογα με την στάθμη των επιφανειακών υδάτων. Αυτό αποτελεί ένα απλό σύστημα ως προς τη λειτουργία του. Ωστόσο εδώ οι διακυμάνσεις των επιπέδων του νερού περιορίζονται από τη μέγιστη διακύμανση της στάθμης των επιφανειακών υδάτων. Ο δεύτερος τρόπος αφορά την έμεση σύνδεση της εγκατάστασης αποθήκευσης όμβριων υδάτων με τα επιφανειακά ύδατα. Σε αυτό το σενάριο, τα όμβρια ύδατα που αποθηκεύονται τροφοδοτούνται από αλλού και επιπλέον αποθηκεύονται και στραγγίζονται με καθυστερημένο ρυθμό. Αυτή η μέθοδος επιτρέπει την αποθήκευση περισσότερης ποσότητας όμβριων υδάτων, καθώς είναι δυνατή η μεγαλύτερη διακύμανση των επιπέδων τους ως προς το επίπεδο του νερού. (Urban Green-Blue Grids for sustainable and resilient cities, Rainwater storage beneath sports fields, accessed on Sept. 2016)Co-benefits and impacts (GR)
Εκτός από το επίπεδο μείωσης της απορροής κατά τη διάρκεια των βροχοπτώσεων και των πλημμυρικών γεγονότων, η αποθήκευση ομβριών υδάτων κάτω από τις αθλητικές εγκαταστάσεις επιτρέπει την πολυλειτουργική χρήση της συγκεκριμένης περιοχής χωρίς να προκαλεί αισθητική αλλοίωση στο τοπίο.Flood management measure
The parent measure, in terms of this measure being a subcategory of the parent one
Last modified: March 10, 2020, 7:19 p.m.


 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά