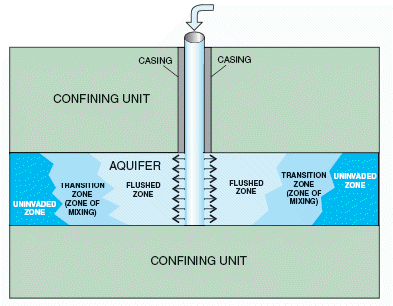
Definition
Aquifer recharge is achieved by adding surface water in basins, furrows, ditches, wells or other facilities where it infiltrates into the soil and recharges the aquifers. Aquifer recharge allows water retention underground. During flood events, water can be redirected to aquifer's area.(Bouwer H., 2001)
Co-benefits and impacts
As water percolates down into the aquifer, it is usually purified from biological pollutants. Being an underground storage solution, it does not require large surfaces of land as does reservoir storage. It reduces evaporation and decreased impact on water resources. Aquifer recharge enhances the flexibility of water utilities concerning (with regards to) the increased risk of floods due to climate change and also can store water during drought periods. Aquifer recharge also helps to replenish water in aquifers.(Smith H., et. al., 2015)
Comments
Aquifer recharge can only be implemented where suitable underground storage is possible. Infiltration basins may not be implemented directly in urban areas due to the pollution risk. Protection measures for the underground storage must be taken in order to preserve it. There is a lack of guidelines for the quality of infiltrated water, which is, to now, regulated locally by each authority. Building up a seawater intrusion barrier may have negative impacts on the environment if the water for the barrier is withdrawn from surface waters, or imported from remote locations. In addition, the equipment may have a high energy demand.(Staub M. and Moreau-Le Golvan Y., 2012)
Definition (GR)
Η επαναπλήρωση του υδροφορέα επιτυγχάνεται προσθέτοντας επιφανειακό νερό σε λεκάνες, αυλάκια, τάφρους, πηγάδια ή άλλες εγκαταστάσεις όπου το νερό διεισδύει στο έδαφος και επαναφορτίζει τους υδροφορείς. Η επαναπλήρωση του υδροφορέα επιτρέπει την κατακράτηση νερού υπογείως. Κατά τη διάρκεια πλημμυρικών γεγονότων, το νερό μπορεί να ανακατευθυνθεί στην περιοχή του υδροφορέα.(Bouwer H., 2001)
Co-benefits and impacts (GR)
Καθώς το νερό διεισδύει στον υδροφορέα, καθαρίζεται συνήθως από βιολογικούς ρύπους. Όντας μια λύση υπόγειας αποθήκευσης, δεν απαιτεί μεγάλες επιφάνειες εδάφους, όπως γίνεται στην αποθήκευση σε δεξαμενές. Μειώνει την εξάτμιση και παρουσιάζει μειωμένες επιπτώσεις στους υδάτινους πόρους.
Η επαναπλήρωση του υδροφορέα ενισχύει την ευελιξία της παροχής νερού (σε σχέση με) τον αυξημένο κίνδυνο πλημμυρών λόγω της κλιματικής αλλαγής και επίσης μπορεί να αποθηκεύει νερό κατά τις περιόδους ξηρασίας. Η επαναπλήρωση του υδροφορέα βοηθά επίσης στην αναπλήρωση του νερού σε υδροφορείς.
(Smith H., et. al., 2015)
Problem types
Case studies
Last modified: May 9, 2020, 11:08 a.m.


 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά